Regional
Widespread telecoms disruptions in Bangladesh as student protests spike
Thursday’s violence in 47 of Bangladesh’s 64 districts killed 27 and injured 1,500, it added, while French news agency AFP put the day’s toll at 32, citing a police spokesman as saying 100 policemen were injured with 50 police booths burnt.
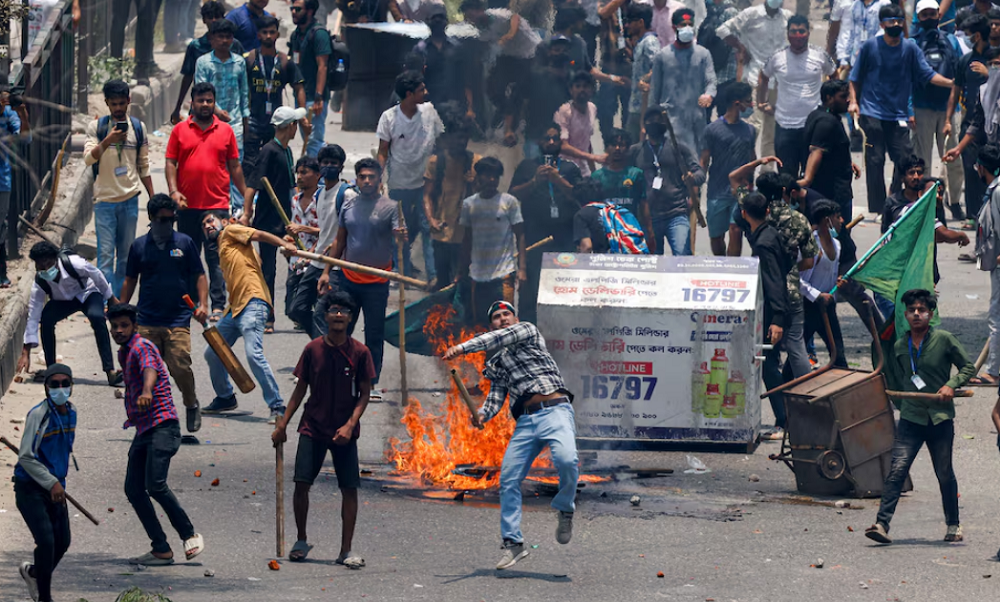
Telecoms links were widely disrupted in Bangladesh on Friday, with television news channels going off the air amid violent student protests against quotas for government jobs that have killed nearly two dozen people this week.
Sparked by student anger against the controversial quotas, the protests, some analysts say, are also being fuelled by economic woes, such as high inflation, growing unemployment and shrinking reserves of foreign exchange, Reuters reported.
The government offered no immediate comment on Friday’s severed communications, but said police in Dhaka, the capital, had barred all public meetings and processions indefinitely.
Police fired tear gas to scatter protesters in some zones of fresh violence, Reuters journalists said, adding that security forces and protesters milled about in the streets of Dhaka.
Protesters blocked roads at many places and threw bricks at security forces, the English-language website of the Bengali newspaper Prothom Alo said.
Thursday’s violence in 47 of Bangladesh’s 64 districts killed 27 and injured 1,500, it added, while French news agency AFP put the day’s toll at 32, citing a police spokesman as saying 100 policemen were injured with 50 police booths burnt.
Reuters, which reported 13 dead, up from a tally of six earlier in the week, could not immediately verify the higher figures.
Citing unidentified sources, India’s Economic Times newspaper said Prime Minister Sheikh Hasina’s government was forced to call in the army late on Thursday to help maintain order.
Reuters could not independently verify the details.
The protests have also opened old and sensitive political faultlines between those who fought for Bangladesh’s independence from Pakistan in 1971 and those accused of collaborating with Islamabad.
The former include the Awami League ruling party of Hasina, who branded the protesters “razakar”, making use of a term that described independence-era collaborators.
Authorities had cut some mobile services on Thursday to try to quell the unrest, but the disruption widened nationwide the next morning, Reuters witnesses said.
Overseas telephone calls and those through the internet were crippled, while the websites of several Bangladesh newspapers did not update on Friday and were also inactive on social media.
A few voice calls went through, but there ws no mobile data or broadband, a Reuters photographer in Dhaka said, adding that even text messages were not being transmitted.
News television channels and state broadcaster BTV went off the air, although entertainment channels were normal, a Reuters witness said.
Some news channels displayed a message blaming technical issues, and promising to resume programming soon, the witness said.
Streets in Dhaka were deserted with little traffic on Friday, a weekly holiday in the Muslim-majority nation, but the witness added that a protest rally had been called for 0800 GMT at the main mosque.
There were no flight disruptions at the main international airport, aviation website Flightradar24 showed.
WEBSITES HACKED
The official websites of the central bank, the prime minister’s office and police appeared to have been hacked by a group calling itself “THE R3SISTANC3”.
“Operation HuntDown, Stop Killing Students,” read identical messages splashed on the sites, adding in crimson letters: “It’s not a protest anymore, it’s a war now.”
Another message on the page read, “Prepare yourselves. The fight for justice has begun,” adding, “The government has shut down the internet to silence us and hide their actions. We need to stay informed about what is happening on the ground.” Giant neighbour India once again urged its citizens in Bangladesh to avoid local travel and limit movement.
The nationwide agitation, the biggest since Hasina was re-elected this year, has been fuelled by high unemployment among the youth, most of them out of education or work, who make up nearly a fifth of a population of 170 million.
Protesters want the government to stop setting aside 30% of government jobs for the families of those who fought for independence from Pakistan.
Bangladesh’s Supreme Court, which has set an Aug.7 date to hear an appeal by Hasina’s government against a high court order last month to reinstate the quota system scrapped in 2018, has suspended the lower court’s order until the hearing.
On Thursday, the government said it was willing to hold talks with the protesters, but they refused, saying, “Discussions and opening fire do not go hand in hand.”
Dhaka’s main university campus had been the site of the worst protests, but Thursday saw bigger demonstrations elsewhere.
Reeling from the ripple effects of the Russia-Ukraine war, Bangladesh got a $4.7-billion bailout from the International Monetary Fund in January 2023.
In June it got immediate access to IMF loans of about $928 million for economic support and about $220 million to fight climate change.
Regional
Imran Khan calls for street movement, urges public to reclaim rights
Khan has appealed for collective action, saying the movement was necessary to restore the rule of law, ensure justice, and end what he described as politically motivated and pre-determined court decisions.
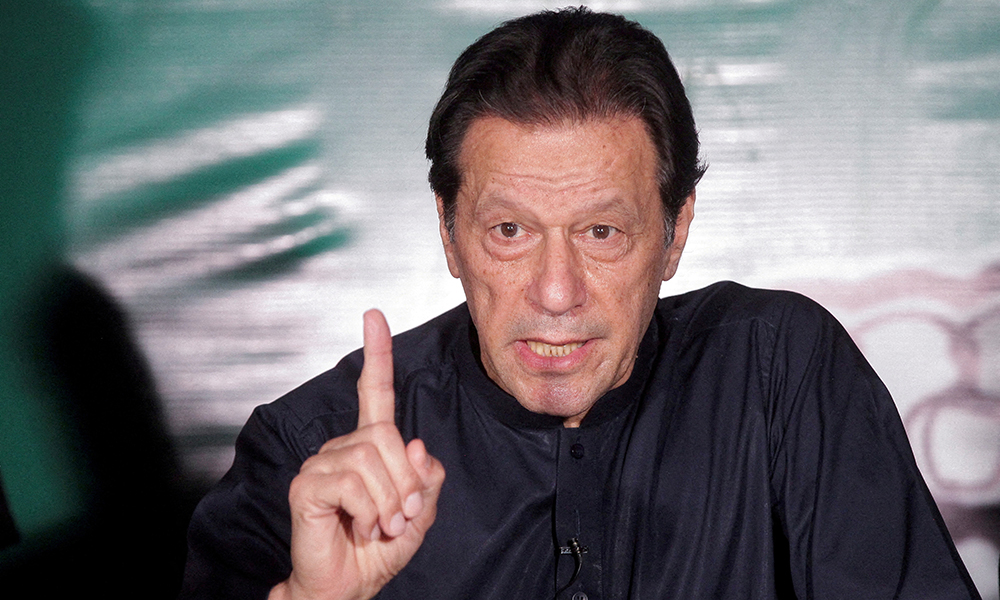

Former Pakistani Prime Minister Imran Khan has called on his supporters and the wider public to prepare for a nationwide street movement, urging citizens to rise in defense of their fundamental rights.
In a message issued from Adiala Jail, where he is currently detained, Khan appealed for collective action, saying the movement was necessary to restore the rule of law, ensure justice, and end what he described as politically motivated and pre-determined court decisions.
Khan said the recent verdict against him was part of sustained political pressure, alleging that the ruling was delivered without due legal process and without giving him a fair opportunity to present his defense. He warned that such practices have severely damaged the credibility of Pakistan’s judicial system.
The former prime minister also called on lawyers, constitutional experts, and members of the legal community to stand with the public and play an active role in safeguarding the Constitution and the rule of law. He said political stability and economic progress were impossible without an independent and impartial judiciary.
Addressing civil-military relations, Khan said his criticism was aimed at individuals rather than institutions. He described the military as belonging to the people of Pakistan, while alleging that actions taken against him in detention were carried out on the instructions of military authorities.
Khan drew comparisons with the 2007 political crisis, warning that continued erosion of the rule of law would have lasting consequences for the country. He praised judges who resist pressure as national heroes and criticized those who, he said, follow orders without question.
The statement comes amid heightened political and judicial tensions in Pakistan, with Khan’s trial and detention continuing to draw strong domestic and international attention.
Regional
Pakistan court hands Imran Khan, wife 17-year jail terms in another graft case
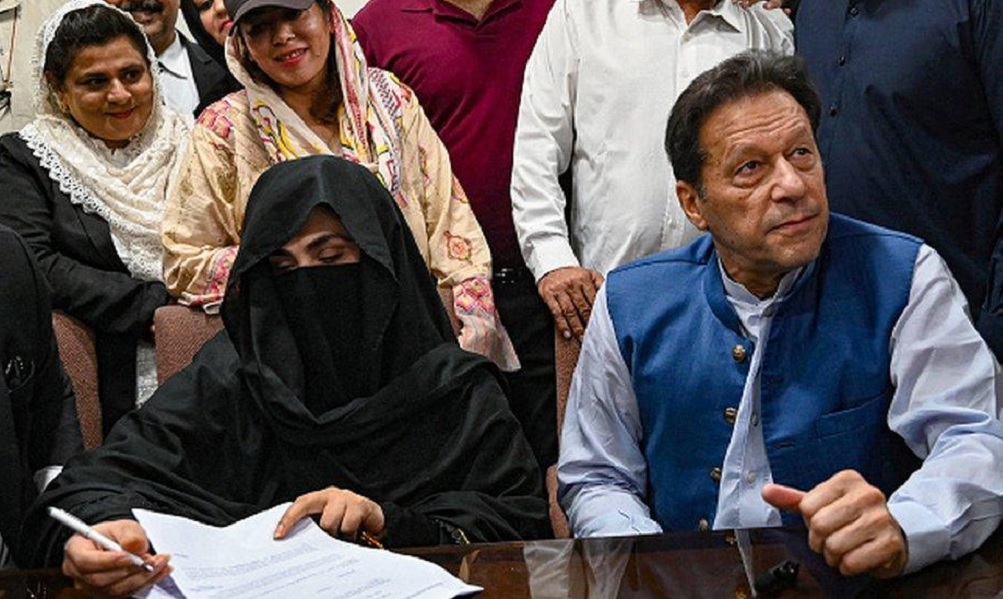

A Pakistani court on Saturday sentenced former Prime Minister Imran Khan and his wife Bushra Bibi to 17 years in prison each in a corruption case involving the under-priced purchase of luxury state gifts, the court and Khan’s lawyers said.
The latest conviction adds to a series of legal troubles for Khan, who has been behind bars since August 2023, and is currently serving a 14-year sentence in a separate land graft case, Reuters reported.
He faces dozens of cases filed since he was ousted from office in 2022, ranging from corruption to anti-terrorism and state secrets charges. Khan has denied wrongdoing in all the cases, which his party says are politically motivated.
“The court announced the sentence without hearing the defence and sentenced 17 years imprisonment to Imran Khan and Bushra Bibi with heavy fines,” Khan’s family lawyer Rana Mudassar Umer told Reuters.
They were handed 10 years’ rigorous imprisonment under Pakistan’s penal code for criminal breach of trust and a further seven years under anti-corruption laws, the special court of Pakistan’s Federal Investigation Agency said in its verdict.
He faces dozens of cases filed since he was ousted from office in 2022, ranging from corruption to anti-terrorism and state secrets charges. Khan has denied wrongdoing in all the cases, which his party says are politically motivated.
“The court announced the sentence without hearing the defence and sentenced 17 years imprisonment to Imran Khan and Bushra Bibi with heavy fines,” Khan’s family lawyer Rana Mudassar Umer told Reuters.
They were handed 10 years’ rigorous imprisonment under Pakistan’s penal code for criminal breach of trust and a further seven years under anti-corruption laws, the special court of Pakistan’s Federal Investigation Agency said in its verdict.
Khan’s jail term from Saturday’s ruling would begin after he has served the 14 years from the land graft case, Information Minister Attaullah Tarar said.
The case relates to luxury watches gifted to Khan by Saudi Arabia’s Crown Prince Mohammed bin Salman during official visits, which prosecutors said Khan and his wife then purchased from the state at a heavily discounted price in violation of Pakistan’s gift rules.
Tarrar said the purchase resulted in losses of several million rupees for the state.
Zulfi Bukhari, a spokesperson for Khan, said the verdict “ignores basic principles of justice” and turns the process into “a tool for selective prosecution.”
Khan has told his legal team to appeal the decision at the Islamabad High Court, Salman Safdar, another one of his lawyers, told reporters outside the jail where the trials were being held, Geo News reported.
ANOTHER STATE GIFTS CONVICTION
The case is separate from an earlier state gifts prosecution linked to Khan’s August 2023 arrest. Earlier sentences of 14 years for Khan and seven years for Bushra Bibi were later suspended on appeal. The couple denies wrongdoing.
The cases are commonly known in Pakistan as the Toshakhana cases, referring to the state repository where gifts received by public officials are deposited.
Following the verdict, Khan’s Pakistan Tehreek-e-Insaf (PTI) party announced plans for protests across Punjab on Sunday.
Khan’s party also says routine family and legal visits have been blocked in recent weeks despite court orders. Authorities deny any mistreatment and say he is receiving all facilities available to prisoners.
Khan, a former cricket star turned politician, remains one of Pakistan’s most polarising figures, with his legal battles unfolding as his Pakistan Tehreek-e-Insaf party remains sidelined from power.
Regional
Pakistan’s military chief Asim Munir in spotlight over Trump’s Gaza plan
Munir was earlier this month anointed chief of the defence forces to head the air force and navy as well, with a job extension until 2030.
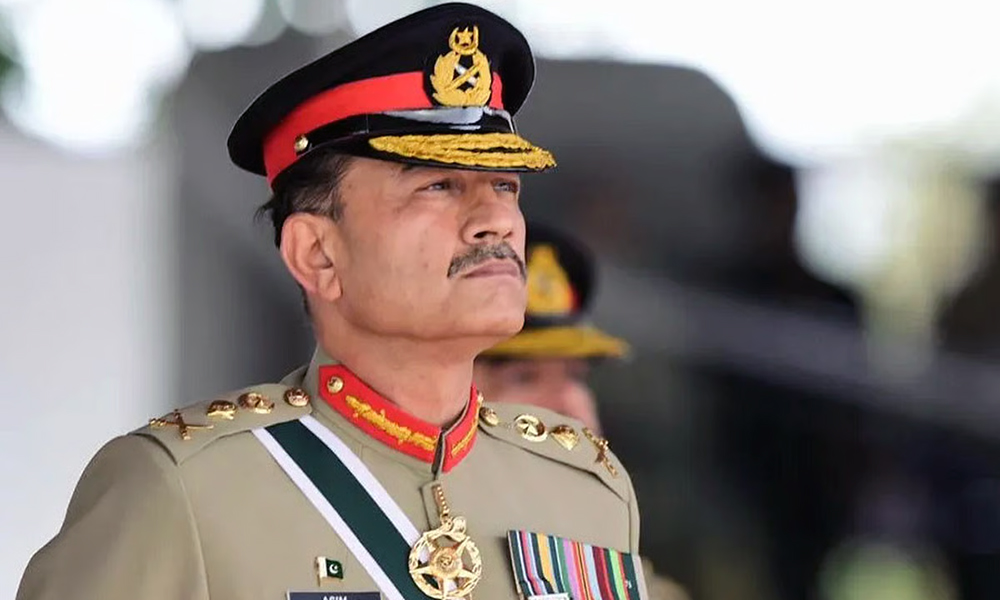

Pakistan’s most powerful military chief in decades faces the toughest test of his newly amassed powers as Washington pushes Islamabad to contribute troops to the Gaza stabilisation force, a move analysts say could spark domestic backlash.
Field Marshal Asim Munir is expected to fly to Washington to meet President Donald Trump in the coming weeks for a third meeting in six months that will likely focus on the Gaza force, two sources told Reuters, one of them a key player in the general’s economic diplomacy.
Trump’s 20-point Gaza plan calls for a force from Muslim nations to oversee a transition period for reconstruction and economic recovery in the war-torn Palestinian territory, decimated by over two years of Israeli military bombardment.
Many countries are wary of the mission to demilitarise Gaza’s Islamist militant group Hamas, which could drag them into the conflict and enrage their pro-Palestinian and anti-Israeli populations.
But Munir has built a close relationship with the mercurial Trump to repair years of mistrust between Washington and Islamabad. In June, he was rewarded with a White House lunch – the first time a U.S. president hosted Pakistan’s army chief alone, without civilian officials.
“Not contributing (to the Gaza stabilisation force) could annoy Trump, which is no small matter for a Pakistani state that appears quite keen to remain in his good graces – in great part to secure U.S. investment and security aid,” said Michael Kugelman, Senior Fellow, South Asia at Washington-based Atlantic Council.
Pakistan, the world’s only Muslim country with nuclear weapons, has a battle-hardened military having gone to war with arch-rival India three times and a brief conflict this summer.
It has also tackled insurgencies in its far-flung regions and is currently embroiled in a bruising war with Islamist militants who it says are operating from Afghanistan.
Pakistan’s military strength means “there is a greater pressure on Munir to deliver his capacity,” said author and defence analyst Ayesha Siddiqa.
Pakistan’s military, foreign office and information ministry did not respond to questions from Reuters. The White House also did not respond to a request for a comment.
Pakistani Foreign Minister Ishaq Dar said last month that Islamabad could consider contributing troops for peacekeeping but disarming Hamas “is not our job.”
Munir was earlier this month anointed chief of the defence forces to head the air force and navy as well, with a job extension until 2030.
He will retain his field marshal title forever, as well as enjoy lifetime immunity from any criminal prosecution under the constitutional amendments that Pakistan’s civilian government pushed through parliament late last month.
“Few people in Pakistan enjoy the luxury of being able to take risks more than Munir. He has unbridled power, now constitutionally protected,” Kugelman added.
“Ultimately, it will be Munir’s rules, and his rules only.”
Over the past few weeks, Munir has met military and civilian leaders from countries such as Indonesia, Malaysia, Saudi Arabia, Turkey, Jordan, Egypt and Qatar, according to the military’s statements, which Siddiqa said appeared to be consultations on the Gaza force.
But the big concern at home is that the involvement of Pakistan troops in Gaza under a U.S.-backed plan could re-ignite protests from Pakistan’s Islamist parties that are deeply opposed to the U.S. and Israel.
The Islamists have street power to mobilise thousands.
A powerful and violent anti-Israel Islamist party that fights for upholding Pakistan’s ultra-strict blasphemy laws was banned in October.
Authorities arrested its leaders and over 1,500 supporters and seized its assets and bank accounts in an ongoing crackdown, officials said.
While Islamabad has outlawed the group, its ideology is still alive.
The party of former jailed premier, Imran Khan, whose supporters won the most seats in the 2024 national elections and has wide public support, also has an axe to grind against Munir.
Abdul Basit, Senior Associate Fellow, S. Rajaratnam School of International Studies in Singapore, said if things escalated once the Gaza force was on the ground, it would cause problems quickly.
“People will say ‘Asim Munir is doing Israel’s bidding’ – it will be foolhardy of anyone not to see it coming.”
-

 Latest News2 days ago
Latest News2 days agoAfghanistan signs 30-year deal for marble mining in Daikundi
-

 Latest News4 days ago
Latest News4 days agoAfghan border forces prevent illegal entry of hundreds into Iran
-

 Latest News3 days ago
Latest News3 days agoPakistan summons Afghan diplomat over deadly attack in North Waziristan
-

 Latest News3 days ago
Latest News3 days agoAfghan health minister calls for medical cooperation between Kabul and New Delhi
-

 Latest News4 days ago
Latest News4 days agoJapan allocates nearly $20 million in humanitarian aid for Afghanistan
-

 Latest News3 days ago
Latest News3 days agoKarzai urges reopening of girls’ schools and universities for Afghanistan’s bright future
-

 Health5 days ago
Health5 days agoAfghanistan seeks India’s support in standardizing traditional medicine
-

 World5 days ago
World5 days agoUS readies new Russia sanctions if Putin rejects peace deal, Bloomberg News reports
























