Science & Technology
US unveils its latest nuclear stealth bomber
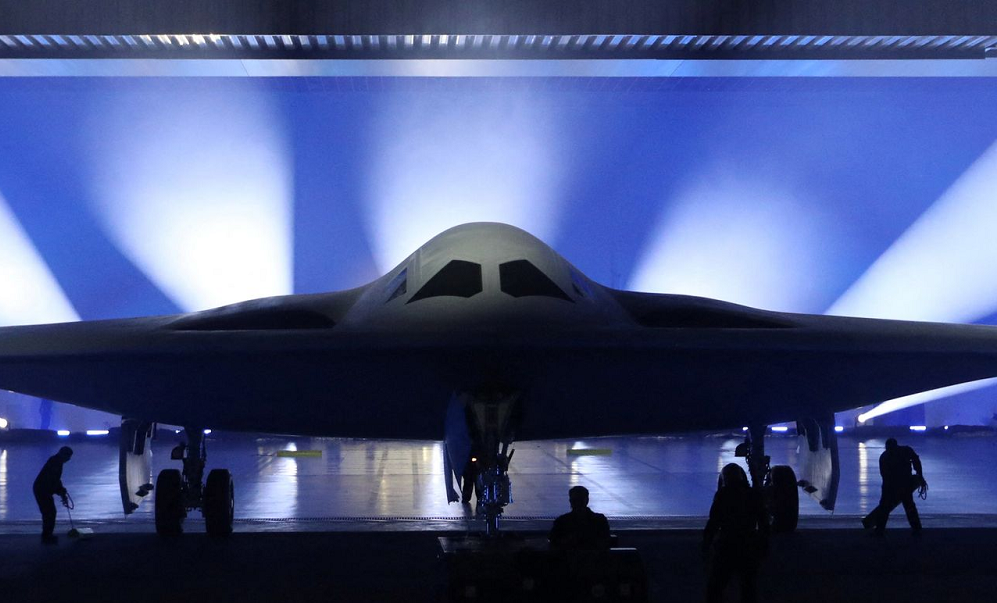

America’s newest nuclear stealth bomber made its debut Friday after years of secret development, and as part of the Pentagon’s answer to rising concerns over a future conflict with China.
The B-21 Raider is the first new American bomber aircraft in more than 30 years. Almost every aspect of the program is classified, Associated Press reported.
As evening fell over the Air Force’s Plant 42 in Palmdale, California, the public got its first glimpse of the Raider in a tightly controlled ceremony. It started with a flyover of the three bombers still in service: the B-52 Stratofortress, the B-1 Lancer and the B-2 Spirit. Then the hangar doors slowly opened and the B-21 was towed partially out of the building.
“This isn’t just another airplane,” Defense Secretary Lloyd Austin said. “It’s the embodiment of America’s determination to defend the republic that we all love.”
The B-21 is part of the Pentagon’s efforts to modernize all three legs of its nuclear triad, which includes silo-launched nuclear ballistic missiles and submarine-launched warheads, as it shifts from the counterterrorism campaigns of recent decades to meet China’s rapid military modernization.
China is on track to have 1,500 nuclear weapons by 2035, and its gains in hypersonics, cyber warfare and space capabilities present “the most consequential and systemic challenge to U.S. national security and the free and open international system,” the Pentagon said this week in its annual China report.
“We needed a new bomber for the 21st Century that would allow us to take on much more complicated threats, like the threats that we fear we would one day face from China, Russia, ” said Deborah Lee James, the Air Force secretary when the Raider contract was announced in 2015.
While the Raider may resemble the B-2, once you get inside, the similarities stop, said Kathy Warden, chief executive of Northrop Grumman Corp., which is building the bomber.
“The way it operates internally is extremely advanced compared to the B-2, because the technology has evolved so much in terms of the computing capability that we can now embed in the software of the B-21,” Warden said.
Other changes include advanced materials used in coatings to make the bomber harder to detect, Austin said.
“Fifty years of advances in low-observable technology have gone into this aircraft,” Austin said. “Even the most sophisticated air defense systems will struggle to detect a B-21 in the sky.”
Other advances likely include new ways to control electronic emissions, so the bomber could spoof adversary radars and disguise itself as another object, and use of new propulsion technologies, several defense analysts said.
“It is incredibly low observability,” Warden said. “You’ll hear it, but you really won’t see it.”
Six Raiders are in production. The Air Force plans to build 100 that can deploy either nuclear weapons or conventional bombs, and can be used with or without a human crew. Both the Air Force and Northrop also point to the Raider’s relatively quick development: The bomber went from contract award to debut in seven years. Other new fighter and ship programs have taken decades.
The cost of the bombers is unknown. The Air Force previously put the price at an average cost of $550 million each in 2010 dollars – roughly $753 million today — but it’s unclear how much is actually being spent. The total will depend on how many bombers the Pentagon buys.
“We will soon fly this aircraft, test it, and then move it into production. And we will build the bomber force in numbers suited to the strategic environment ahead,” Austin said.
Ellsworth Air Force Base in South Dakota will house the bomber’s first training program and squadron, though the bombers are also expected to be stationed at bases in Texas and Missouri.
Science & Technology
Skype ends operations after 22 years of service
Microsoft acquired Skype in 2011 and says the decision is part of a strategy to focus on its other platform, Microsoft Teams.

Skype officially shut down on Monday. The closure comes after nearly 22 years in operation, during which Skype became known for making international voice and video calls accessible and affordable for millions of people worldwide.
Microsoft acquired Skype in 2011 and says the decision is part of a strategy to focus on its other platform, Microsoft Teams.
Launched in 2003, Skype quickly became a revolutionary tool for free voice and video calls over the internet, amassing more than 300 million monthly users at its peak in the mid-2010s. The free platform changed how people communicated across borders, long before Zoom or FaceTime.
In 2011, Microsoft acquired Skype for $8.5bn, aiming to make it a central part of its communications strategy. But as competitors like WhatsApp, Zoom, and eventually Microsoft’s own Teams gained traction, Skype’s popularity faded.
On February 28, Microsoft said it would retire Skype on May 5 to streamline its services and prioritise Teams for communication and collaboration.
Microsoft has urged users to transition to Teams by visiting skype.com and utilising the “Start using Teams” feature. All Skype chats and contacts will remain accessible through Teams using the same login credentials.
Science & Technology
Apple moving to make most iPhones for US in India rather than China

Apple aims to make most of its iPhones sold in the United States at factories in India by the end of 2026, and is speeding up those plans to navigate potentially higher tariffs in China, its main manufacturing base, Reuters reported.
The U.S. tech giant is holding urgent talks with contract manufacturers Foxconn and Tata to achieve that goal, the person, who declined to be named as the planning process is confidential, said on Friday.
Apple and Foxconn did not immediately respond to requests for comment, while Tata declined to comment.
Apple sells over 60 million iPhones in the U.S. annually with roughly 80% of them made in China currently.
Prime Minister Narendra Modi has in recent years promoted India as a smartphone manufacturing hub, but higher duties on importing mobile phone parts compared to many other countries means it is still expensive for companies to produce in India.
For iPhones, manufacturing costs in India are 5-8% higher than in China, with the difference rising to as much as 10% in some cases, the source said.
Apple has already stepped up production in India to beat U.S. President Donald Trump’s tariffs, shipping some 600 tons of iPhones worth $2 billion to the United States in March. The shipments from India marked a record for both its contractors Tata and Foxconn, with the latter alone accounting for smartphones worth $1.3 billion, Reuters reported last week.
In April, the U.S. administration imposed 26% duties on imports from India, much lower than the more than 100% China was facing at the time. Washington has since paused most duties for three months, except for China.
Trump’s administration has since signalled openness to de-escalating the trade war between the world’s two largest economies that has raised fears of recession.
The Financial Times first reported about Apple’s plan on Friday.
As Apple diversifies its manufacturing beyond China, it has positioned India for a critical role. Foxconn and Tata, its two main suppliers there, have three factories in all, with two more being built.
Science & Technology
China, Russia may build nuclear plant on moon to power lunar station, official says
Russia’s space agency Roscosmos said last year it planned to build a nuclear reactor on the moon’s surface with the China National Space Administration (CNSA) by 2035 to power the ILRS.
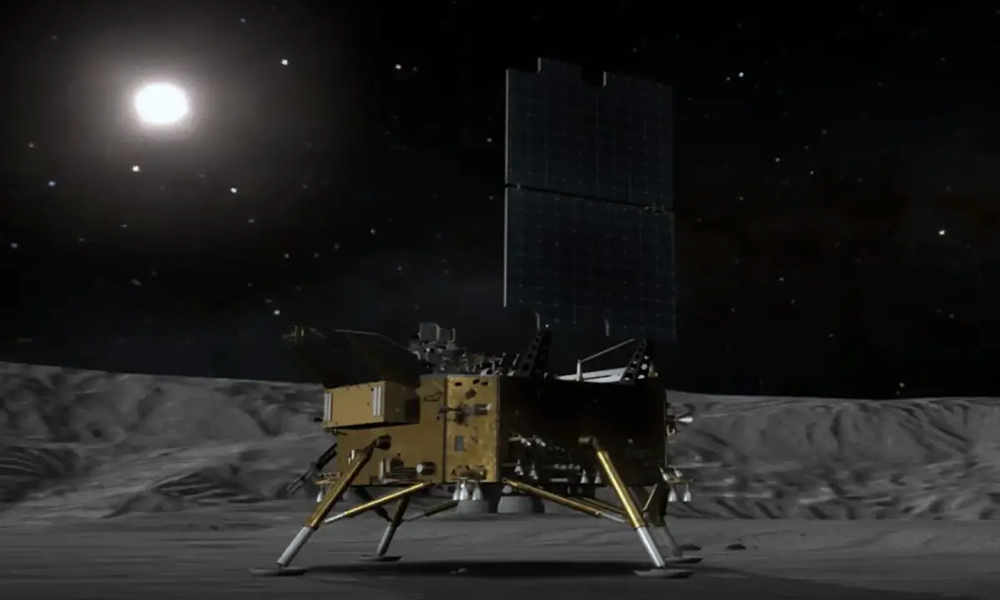

China is considering building a nuclear plant on the moon to power the International Lunar Research Station (ILRS) it is planning with Russia, a presentation by a senior official showed on Wednesday.
China aims to become a major space power and land astronauts on the moon by 2030, and its planned Chang’e-8 mission for 2028 would lay the groundwork for constructing a permanent, manned lunar base.
In a presentation in Shanghai, the 2028 mission’s Chief Engineer Pei Zhaoyu showed that the lunar base’s energy supply could also depend on large-scale solar arrays, and pipelines and cables for heating and electricity built on the moon’s surface.
Russia’s space agency Roscosmos said last year it planned to build a nuclear reactor on the moon’s surface with the China National Space Administration (CNSA) by 2035 to power the ILRS.
The inclusion of the nuclear power unit in a Chinese space official’s presentation at a conference for officials from the 17 countries and international organisations that make up the ILRS suggests Beijing supports the idea, although it has never formally announced it.
“An important question for the ILRS is power supply, and in this Russia has a natural advantage, when it comes to nuclear power plants, especially sending them into space, it leads the world, it is ahead of the United States,” Wu Weiren, chief designer of China’s lunar exploration program, told Reuters on the sidelines of the conference.
After little progress on talks over a space-based reactor in the past, “I hope this time both countries can send a nuclear reactor to the moon,” Wu said.
China’s timeline to build an outpost on the moon’s south pole coincides with NASA’s more ambitious and advanced Artemis programme, which aims to put U.S. astronauts back on the lunar surface in December 2025.
Wu said last year that a “basic model” of the ILRS, with the Moon’s south pole as its core, would be built by 2035.
In the future, China will create the “555 Project,” inviting 50 countries, 500 international scientific research institutions, and 5,000 overseas researchers to join the ILRS.
Researchers from Roscosmos also presented at the conference in Shanghai, sharing details about plans to look for mineral and water resources, including possibly using lunar material as fuel.
The ILRS preceded Russia’s invasion of Ukraine in 2022 but incentives for cooperation between Roscosmos and CNSA have increased since the outbreak of the war, according to Chinese analysts.
With China’s rapid technological advances and lunar achievements, and as Western sanctions prevent Roscosmos from many imports of space technology and equipment, China can now “alleviate the pressure” on Russia and help it “achieve new breakthroughs in satellite launches, lunar exploration, and space stations,” Liu Ying, a researcher at the Chinese foreign ministry’s diplomatic academy, wrote in a journal article last year.
-

 Regional5 days ago
Regional5 days agoAt least 26 civilians killed in Indian strikes on Pakistan: Islamabad
-

 Regional5 days ago
Regional5 days agoIndia strikes Pakistan over Kashmir tourist killings
-

 Science & Technology5 days ago
Science & Technology5 days agoSkype ends operations after 22 years of service
-

 Latest News5 days ago
Latest News5 days agoIslamic Emirate of Afghanistan ‘concerned’ over rising tensions between Pakistan and India
-

 Latest News4 days ago
Latest News4 days agoPassport Directorate earns nearly 13 billion AFN in one year
-

 World5 days ago
World5 days agoMacron to meet Syrian president on Wednesday, expected to discuss security
-
 Health5 days ago
Health5 days agoWHO confirms second Polio case in Afghanistan
-

 Regional4 days ago
Regional4 days agoIndia dismisses report of Pakistan downing jets as “disinformation”
























