Latest News
UN Security Council hears how IEA bans on women are ‘obscuring’ positive achievements
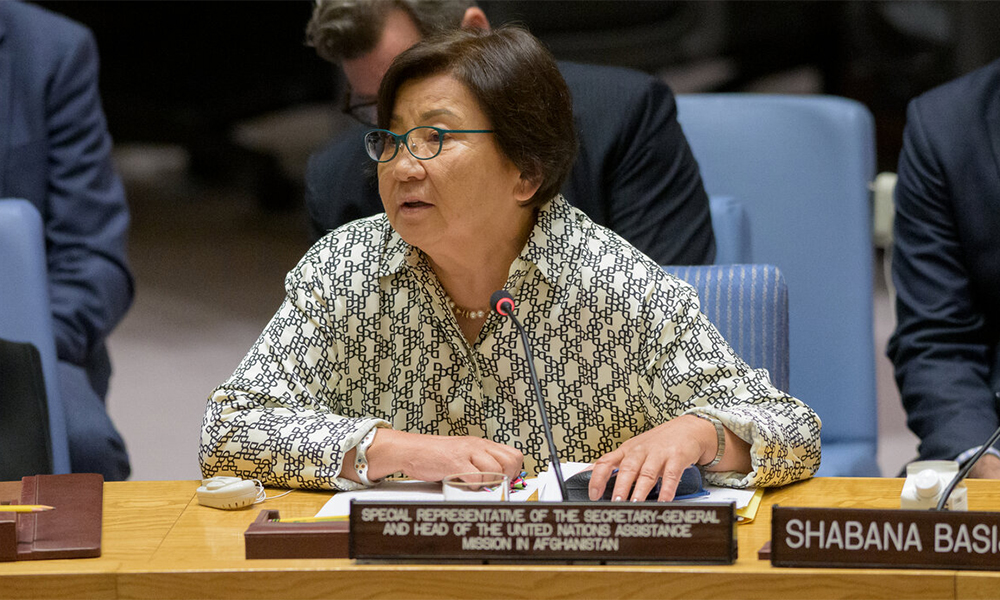

The UN Secretary-General’s Special Representative for Afghanistan, Roza Otunbayeva said on Wednesday that the bans affecting women and girls in the country were “obscuring” some of the other more positive achievements that have taken place under the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan (IEA).
She said UNAMA continues to face a “complicated situation in Afghanistan,” and that restrictions against Afghan women working for the United Nations places a question mark over the organization’s activities across the country.
Briefing the UN Security Council, Otunbayeva said: “We have been given no explanations by the de facto authorities for this ban and no assurances that it will be lifted.”
She stated UNAMA will not put their national female staff in danger, and therefore have stopped them from reporting to work since the ban was imposed in April. All male national staff performing non-essential tasks are also still at home.
Otunbayeva went on to say, the UN in Afghanistan is “steadfast” over their decision that “female national staff will not be replaced by male national staff as some de facto authorities have suggested.”
She said: “The Taliban (Islamic Emirate) ask to be recognized by the United Nations and its members, but at the same time they act against the key values expressed in the United Nations Charter.”
On positive changes identified, she said: “One of these is the growing evidence that the Taliban’s ban on opium cultivation, announced in April last year, has been effectively enforced in many parts of the country. According to initial media reports, cultivation of opium has significantly decreased.”
She added however that at the same time, the opium economy has helped sustain parts of the rural economy in Afghanistan. “Donors should consider allocating funding to alternative livelihood programmes that address the specific needs of farmers affected by the ban,” she said.
Otunbayeva also pointed out that the Afghan economy remains stable, albeit at a low equilibrium and that according to the World,
inflation is declining and the exchange rate remains steady.
“In part this is due to the welcome reduction of high-level corruption. The de facto authorities continue to report the collection of sufficient revenues to finance government operations, including paying civil service salaries,” she said.
However, this macro-economic stability, coexists with severe household poverty. She said 58 percent of households struggle to satisfy basic needs and that humanitarian efforts continue to address the needs of the nearly 20 million people.
She warned that given the drop in donor funding, United Nations cash shipments, required for humanitarian operations, are expected to decrease.
She went on to say that the IEA is making concerted counter-terrorism efforts, particularly with Daesh. Despite this, attacks have taken place, she said.
Otunbayeva also stated that while the end of the armed conflict has greatly reduced the number of civilian casualties since the IEA came to power, the United Nations Mine Action Service in Afghanistan estimates around 100 casualties per month from unexploded ordnance.
According to her, UNAMA is “greatly concerned by Afghanistan’s vulnerability to climate change. Years of drought have compounded the effects of conflict and poverty. Climate change is fostering population displacements inside Afghanistan that could be destabilizing,” she said adding that in order to address Afghanistan’s lack of water and consequent food insecurity, the IEA has begun digging a canal that will divert waters from the northern Amu Darya river, raising the concerns of neighboring countries.
“Overall the need to mitigate the effects of climate change requires a more specific dialogue between the de facto authorities and the international community,” she said.
Latest News
Mines ministry says work on TAPI project to speed up as weather improves
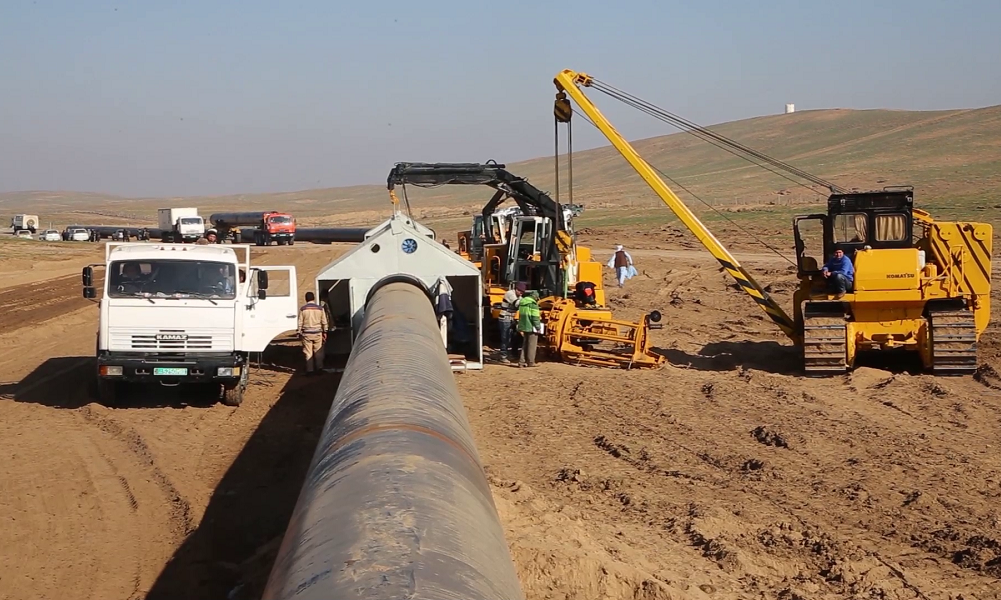

Homayoun Afghan, the spokesperson for the Ministry of Mines and Petroleum, says with rising temperatures in the country, work on the TAPI pipeline project will accelerate. He added that all partners involved in the TAPI project are eager to expedite progress.
He emphasized that since the launch of the project’s practical work, 1,700 kilometers of the TAPI gas pipeline route have been surveyed, and 9 kilometers of pipeline have already been laid within Afghan territory.
The ministry officials stated that the expansion of the TAPI project will create hundreds of new jobs for citizens in operational, security, technical, and logistical sectors of the project.
“First, this project will help create jobs for Afghans. Second, it will strengthen Afghanistan’s economy. Third, we can derive direct positive benefits from this project,” said Mohammad Bani Afghan, an economic expert.
Economic experts further highlighted that once the project is operational, Afghanistan is expected to earn approximately $400 million annually in transit fees. Additionally, the project will spur economic growth and reduce unemployment rates in the country.
Latest News
Pakistan to file complaint with UN against IEA and India
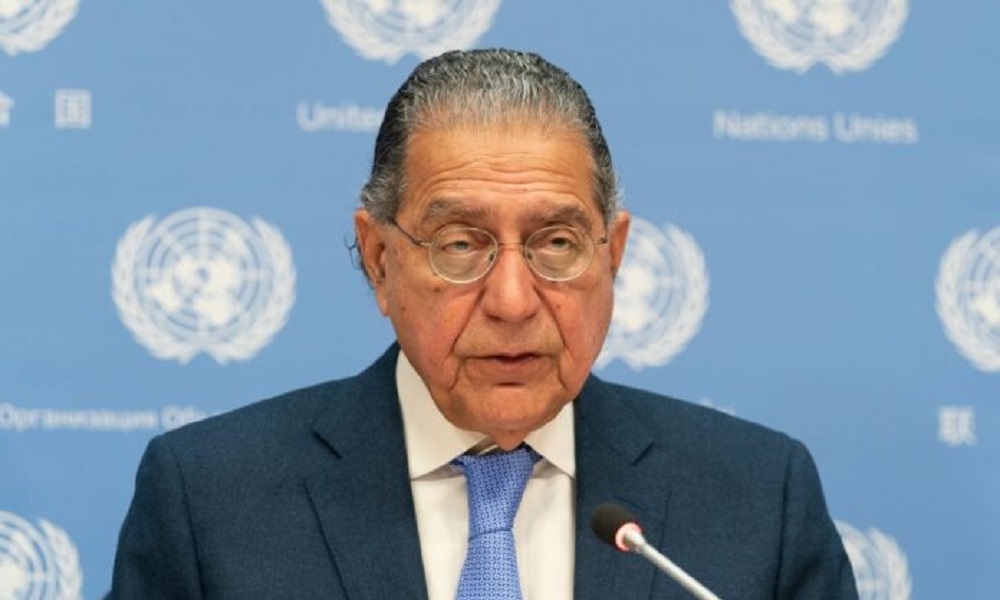

Pakistan’s Permanent Representative to the United Nations, Munir Akram, says Islamabad will submit a complaint to the UN against the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan (IEA) and India for “supporting terrorism.”
In an interview with Pakistani media, Akram alleged that IEA was involved in the attack on the Jaffar Express train.
He claimed, “There is evidence against the Taliban government [Islamic Emirate]. This time, we have traced communications and compiled evidence that we will certainly present. Even previously, if you review the latest report by the UN’s Counter-Terrorism Monitoring Team, it was clear that terrorism originates from Afghanistan, and the government there is involved in this matter.”
The Pakistani diplomat further accused India of using Afghan soil to promote terrorism.
Meanwhile, Pakistan’s military spokesperson, Ahmed Sharif Chaudhry, asserted during a press briefing that terrorists involved in the recent train incident and prior attacks had used weapons of Indian and Afghan origin.
“The terrorists behind the train attack in Balochistan and previous incidents used Indian-made weapons and arms left behind in Afghanistan. We must recognize that the primary backer of this Balochistan terrorist attack and past events is our eastern neighbor [India]. Militants based in Afghanistan have consistently fueled instability in Pakistan,” said Chaudhry.
However, experts argue that Pakistani authorities, grappling with weak governance in ensuring citizen security, are attempting to deflect blame onto Afghanistan to obscure their own inefficiencies.
Meanwhile, the Islamic Emirate has strongly denied any involvement in Pakistan’s security challenges, particularly the recent Balochistan attack, dismissing the allegations as baseless.
IEA has repeatedly urged Pakistani officials not to attribute their domestic security failures to Afghanistan.
Latest News
Trump says he would have kept Bagram Air Base
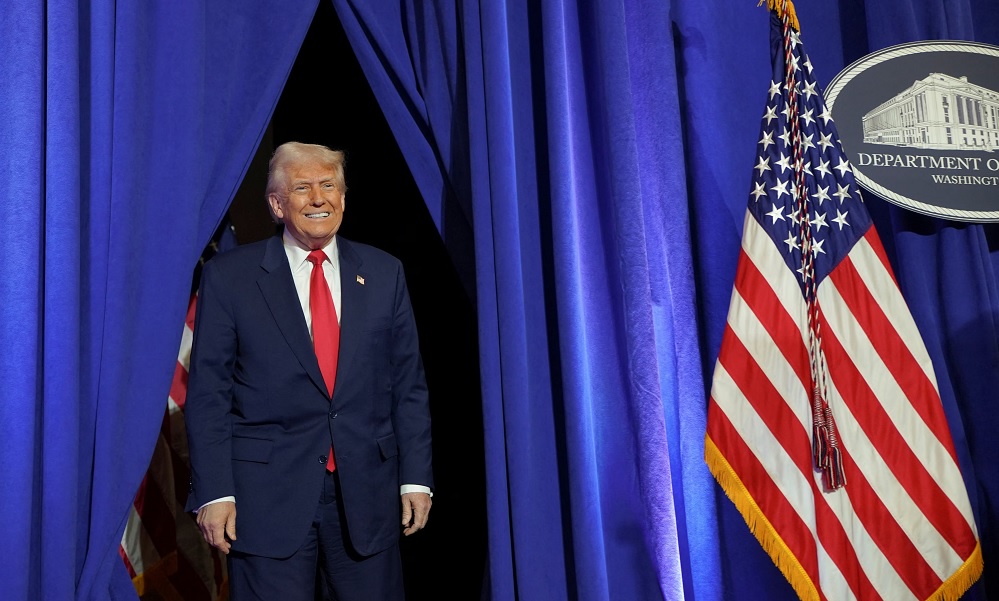

US President Donald Trump has once again said that if he had remained the president, Bagram Air Base in Afghanistan would have been kept due to its proximity to China.
In his speech on Friday at the US Department of Justice, Trump claimed that Bagram Airfield is now occupied by China.
He also said that the withdrawal of the United States from Afghanistan in the way it was done was “the most humiliating time” in the history of the United States.
“I would have been out faster than them. I was the one that got it down to the right level. but we would have kept Bagram, the big Air Force base. We would have kept it. Right now, China occupies Bagram and the reason we would have kept it is because it is one hour away from where China has and builds its nuclear missiles and weapons,” Trump said.
“And they gave that up in the dark of night, they left the lights on and they left the dogs behind. By the way, a lot of people say what about all the dogs. They had a lot of dogs and they left the dogs behind and what a shame, what a shame. The way we got out, I think it was the most humiliating time in the history of our country,” he added.
Trump said that if he had remained the president, the US would have left Afghanistan “with dignity and strength.”
He suggested the way the US withdrew from Afghanistan probably got Russia attack Ukraine.
The Islamic Emirate has previously rejected Trump’s claim that China has seized Bagram Airfield.
-
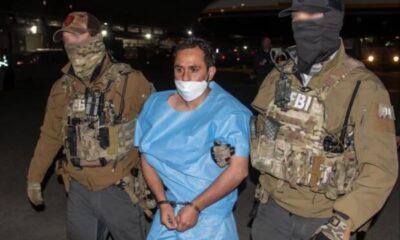
 Latest News4 days ago
Latest News4 days agoKabul Airport bombing suspect not a top-level planner of deadly attack: FBI
-

 World5 days ago
World5 days agoZelenskiy in Saudi Arabia as US voices hope for Ukraine peace talks
-

 World4 days ago
World4 days agoPhilippines’ ex-President Duterte arrested at ICC’s request over ‘drugs war’ killings
-

 World4 days ago
World4 days agoIran’s President to Trump: I will not negotiate, ‘do whatever the hell you want’
-

 Latest News5 days ago
Latest News5 days agoAfghanistan’s foreign minister meets with Omani counterpart for talks
-

 Sport4 days ago
Sport4 days agoAsian Cup: Afghanistan’s beach soccer team arrives in Thailand
-

 Latest News3 days ago
Latest News3 days agoIndia says ‘special’ ties have been foundation of engagement with Afghanistan
-

 Sport3 days ago
Sport3 days agoCricket Ireland cancels Afghanistan series for ‘financial reasons’
























