Climate Change
Sydney beats 1950 rainfall record with 3 wet months to spare

Australia’s largest city, Sydney, has been soaked by its wettest year on record with almost three months of expected above-average rain to spare.
The city of 5 million people beat its 1950 record of 2,194 millimeters (86.4 inches) at 12:30 p.m. on Thursday when 27.2 mm (1.07 in) of rain had fallen at the Observatory Hill rain gauge since morning, Australia’s Bureau of Meteorology said. Records at Observatory Hill go back to 1859, AP reported.
Heavy rain is forecast to continue across Sydney and other parts of southeast Australia, peaking on Saturday.
The Bureau of Meteorology last month declared that a La Niña weather pattern, which is associated with above-average rainfall in eastern Australia, was underway in the Pacific.
The bureau forecast that the La Niña event may peak during the current Southern Hemisphere spring and return to neutral conditions early next year.
La Niña is the cooler flip side of the better-known drying El Niño pattern. La Niña occurs when equatorial trade winds become stronger, changing ocean surface currents and drawing up cooler deep water.
It is the third La Niña since 2019 became Australia’s hottest and driest year on record.
That year came to a catastrophic conclusion with wildfires fueled by drought that directly or indirectly killed more than 400 people, destroyed more than 3,000 homes and razed 19 million hectares (47 million acres) of woods, farmland and city fringes.
Sydney was among several southeast Australian cities that were shrouded in acrid wildfire smoke during the Southern Hemisphere summer of 2019-20.
Sydney had its wettest July on record this year after only two weeks, passing the 1950 record of 336.1 mm (13.2 in) on the way to a total of 404 mm (15.9 in).
March broke a 1942 record of 521.4 mm (20.5 in) when 554 mm (21.8 in) of rain fell.
The ongoing deluge will see rivers in New South Wales state swollen by moderate-to-major flooding, affecting towns including Tamworth, Dubbo and Bathurst, authorities said.
Climate Change
Powerful earthquake of 6.2 magnitude shakes Istanbul

A strong earthquake with a magnitude of 6.2 shook Istanbul on Wednesday, Turkey’s AFAD disaster agency said, one of the strongest quakes to strike the city of 16 million in recent years.
There were no immediate reports of damage, but people evacuated buildings as the quake hit and shook the city, located on the European and Asian shores of the Bosphorus strait.
The epicentre of the quake, which struck at 12:49 (0949 GMT) was in the area of Silivri, some 80 km (50 miles) to the west of Istanbul. It was at a depth of 6.92 km (4.3 miles), AFAD said.
Broadcaster TGRT reported that one person had been injured as a result of jumping off a balcony during the quake, which occurred during a public holiday in Turkey.
AFAD warned people in the region against entering damaged buildings.
The German Research Centre for Geosciences (GFZ) said the earthquake had a magnitude 6.02. It was at a depth of 10 km (6.21 miles) GFZ said.
(Reuters)
Climate Change
Tornadoes, heavy rains rip across central, southern US
Millions of people are under alerts for tornadoes and flash floods and dangers will continue into early Thursday
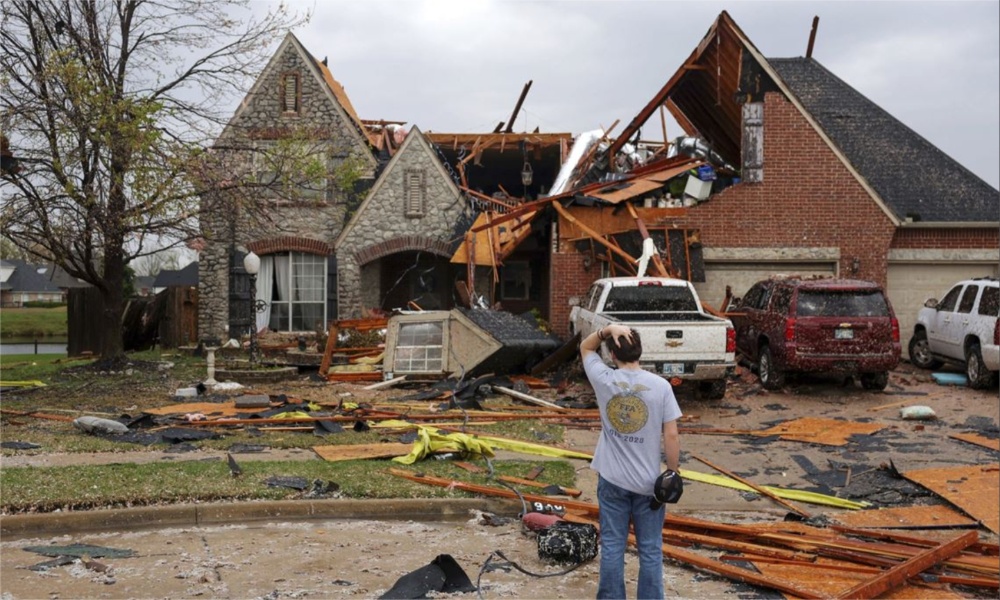

Tornadoes ripped across a wide swath of central and southern United States on Wednesday, destroying homes and businesses and bringing down power lines and trees.
The National Weather Service said there had been at least 15 reports of tornadoes in at least four states by late Wednesday.
Eight people have been injured across Kentucky and Arkansas, including one critically injured in Kentucky’s Ballard County, local officials said.
Late Wednesday, Arkansas Governor Sarah Huckabee Sanders declared a state of emergency across the state due to the storms, which also brought hail and torrential rain, Reuters reported.
The NWS said millions of people were under alerts for tornadoes and flash floods and that dangers would continue into early Thursday.
Violent storms are forecast to ravage the country for several days, the NWS said, with Wednesday just “the beginning of a multi-day catastrophic and potentially historic heavy rainfall event.”
“The word for tonight is ‘chaotic’,” said Scott Kleebauer, a NWS meteorologist. “This is a large expanse of storms migrating slowly to the east, stretching from southeast Michigan down into southeastern Arkansas.”
The town of Nevada, Missouri, was hit by a tornado. Writing on social media, the state’s Emergency Management Agency said it caused “major damage to several businesses, power poles were snapped and several (empty) train cars were flipped onto their sides by the powerful storm!”
The NWS issued tornado and flash flood warnings for parts of Missouri, Arkansas, Tennessee, Mississippi, Indiana, Illinois, Kentucky and Oklahoma.
It called the rain threats for Arkansas, Missouri, Tennessee and Mississippi in the coming days a “generational flood event” with some locations forecast to see as much as 15 inches (38.1 cm) of rain by the weekend, which could cause rivers to burst their banks and cause “catastrophic river flooding.”
More than 400,000 customers had their power knocked out across the storm-hit area, according to PowerOutage.us.
Climate Change
UN urges aid to Myanmar quake survivors before monsoons hit, death toll climbs towards 3,000
Aid groups in Myanmar warned that the window to find survivors was closing fast.
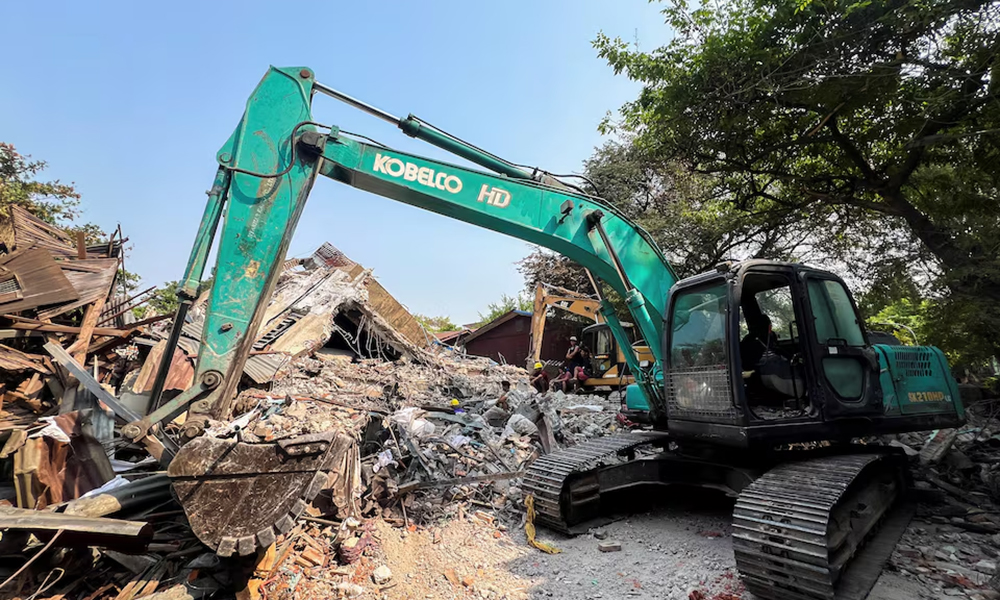

United Nations officials who surveyed earthquake damage in Myanmar urged the global community on Tuesday to ramp up aid before the looming monsoon season worsens already catastrophic conditions, with the death toll at 2,719 and expected to surpass 3,000.
Drinking water, hygiene, food, shelter and medicine are the most critical needs following extensive damage to buildings, roads and bridges, said Marcoluigi Corsi, acting humanitarian and resident coordinator following a two-day visit.
“We remain, of course, deeply committed to reaching people in Myanmar who need aid,” U.N. spokesperson Stephane Dujarric said. “And we must act swiftly to provide relief before the upcoming monsoon season, which, of course, will even worsen this horrendous crisis.”
A civil war in Myanmar had displaced more than 3 million people long before the quake struck. U.N. Special Envoy for Myanmar Julie Bishop urged all sides to immediately cease fire, permit humanitarian access and ensure aid workers are safe.
“Continuing military operations in disaster-affected areas risks further loss of life,” she said in the statement.
Aid groups in Myanmar warned that the window to find survivors was closing fast.
Myanmar’s military ruler Min Aung Hlaing said the death toll from Friday’s 7.7 magnitude quake reached 2,719 as of Tuesday morning and was expected to surpass 3,000. Some 4,521 people were injured and 441 missing.
“Among the missing, most are assumed to be dead. There is a narrow chance for them to remain alive,” he said in a speech.
The quake, which struck at lunchtime on Friday, was the strongest to hit the Southeast Asian country in more than a century. It toppled ancient pagodas and modern buildings alike and inflicted significant damage on Myanmar’s second city Mandalay and Naypyitaw, the capital the previous junta purpose-built to be an impregnable fortress.
U.N. agencies said hospitals were overwhelmed and rescue efforts hindered by infrastructure damage and the civil war. Rebels have accused the military of conducting airstrikes even after the quake and on Tuesday a major rebel alliance declared a unilateral ceasefire to help relief efforts.
The earthquake was the latest in a succession of blows for the impoverished country of 53 million people following a 2021 coup that returned the military to power and devastated the economy after a decade of development and tentative democracy.
Myanmar’s military has been accused of widespread atrocities against civilians as it fought to quell a multi-pronged rebellion after the coup. It has dismissed the accusations as misinformation and says it is protecting the country from terrorists.
In neighbouring Thailand, the death toll from the quake rose to 21 on Tuesday, with hundreds of buildings damaged. Rescuers kept searching for life in the rubble of a collapsed skyscraper under construction in the capital Bangkok, but acknowledged time was against them.
The region has been hit by five more aftershocks.
Julia Rees of the U.N. children’s agency UNICEF said she witnessed entire communities in Myanmar that had been flattened, with immense destruction and psychological trauma.
“And yet, this crisis is still unfolding. The tremors are continuing. Search and rescue operations are ongoing. Bodies are still being pulled from the rubble,” she said in a statement.
“Let me be clear: the needs are massive, and they are rising by the hour. The window for life-saving response is closing.”
In the Mandalay area, 50 children and two teachers were killed when their preschool collapsed, the U.N. humanitarian agency said.
In a rare survival story, a 63-year-old woman who was trapped for 91 hours was pulled from the rubble of a building in Naypyitaw on Tuesday in a joint rescue effort by the Myanmar fire department and teams from India, China and Russia.
Myanmar’s civil war has complicated efforts to reach those injured and made homeless, including tight controls over the internet and communication networks.
The Three Brotherhood Alliance of three major rebel groups at war with the junta on Tuesday declared a unilateral one-month ceasefire, to allow urgent humanitarian efforts to “be carried out as swiftly and effectively as possible”.
In its nightly news bulletin on Tuesday, state-controlled MRTV quoted Min Aung Hlaing as saying the military had halted its offensives but unspecified ethnic minority armies were planning to exploit the disaster.
“The military is aware they are gathering, training, and preparing to attack,” it said, quoting the general as saying at an event to raise funds for quake victims. “We consider it as attacking us and will respond accordingly.”
One rebel group, the Karen National Union, on Sunday said the junta had conducted airstrikes in the east of the country at a time when it should be prioritising quake relief efforts.
Amnesty International said it had received testimony corroborating reports of air strikes near areas where quake recovery efforts were focused.
“You cannot ask for aid with one hand and bomb with the other,” said Amnesty’s Myanmar researcher Joe Freeman.
It was unclear if Min Aung Hlaing would make a rare foreign trip this week to attend a regional summit in Bangkok as planned. Thailand’s on Tuesday said the general may attend by teleconference.
In Bangkok, rescuers were still seeking signs of life in the ruins of an unfinished skyscraper that collapsed, aware that four days after the quake, chances had dimmed of finding survivors.
Fourteen deaths have been confirmed at the site and seven elsewhere in the city. The government is investigating the collapse and initial tests showed some steel samples from the site were substandard.
There were an estimated 70 bodies under the rubble and experts said 12 had been located using scanners, but access was blocked by large debris.
“Maybe they can survive one week or two weeks, so we have to go on,” Bangkok Governor Chadchart Sittipunt said. “The experts still have hope.”
-

 Sport5 days ago
Sport5 days agoAfghanistan qualify for U19 Cricket World Cup 2026
-

 Regional5 days ago
Regional5 days agoDeadliest US strike in Yemen kills 74 at oil terminal, Houthis say
-

 World4 days ago
World4 days agoThousands of protesters rally against Trump across US
-

 World4 days ago
World4 days agoIran, US end nuclear talks in Rome, agree to meet next week
-
 Latest News4 days ago
Latest News4 days agoPolio vaccination campaign launched in Afghanistan
-

 International Sports4 days ago
International Sports4 days agoIPL 2025: 14-year-old Vaibhav Suryavanshi becomes youngest IPL player
-

 International Sports2 days ago
International Sports2 days agoIPL 2025: Robo-Dog ‘Champak’ explained
-

 Latest News3 days ago
Latest News3 days agoChina invites various Afghan delegations to attend Shanghai forums






















