Latest News
Pakistan to send back ‘registered refugees’ after deporting illegal immigrants
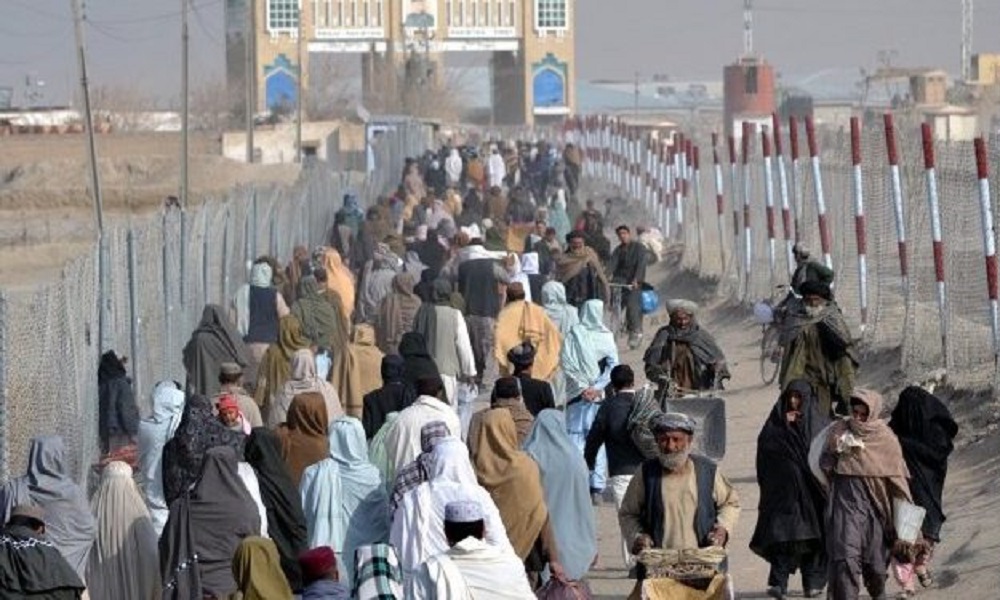

Pakistan will begin the process of returning “registered refugees” to their home countries once it completes the deportation of all illegal immigrants in the country, Balochistan's acting Minister for Information Jan Achakzai said on Thursday, amid nationwide sweeps to round up foreigners staying illegally in the South Asian country.
"So far, 80,000 immigrants from Balochistan have left Pakistan. After this, [we] will send back the registered refugees as well," Achakzai said while addressing a press conference in Karachi.
Jan Achakzai stated that this decision is a response to the use of Afghan soil by hostile elements for terrorist activities in Pakistan. However, the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan has always rejected such allegations.
Achakzai stated that Pakistan intends to initiate a similar process of expelling immigrants with legal documents living in the country.
This Pakistani official also emphasized that the process of expelling “illegal” refugees will continue even after Pakistan’s upcoming elections in February next year.
Jan Achakzai said, “No one should make a mistake. This decision is made by an ‘independent government’ to repatriate all illegal immigrants. Therefore, any government that comes into power after the elections will continue this policy.”
He claimed that terrorists use Afghan territory to target Pakistan’s security forces. Therefore, Pakistan has decided to send back “illegal” immigrants to their country of origin.
Achakzai clarified that six “terrorists” killed in the city of Zhob in Balochistan last week were Afghan citizens.
He once again stressed that with the IEA’s takeover of Afghanistan, terrorist attacks in Pakistan have increased.
Achakzai noted that the Balochistan government blocked around one hundred thousand fake Pakistani national identity cards, with an additional twenty thousand blocked in Sindh.
The Minister of Information for Balochistan stated that 80,000 Afghan migrants have been expelled from the province, with plans to accelerate this process. Meanwhile, reports indicate that a UN High Commissioner for Refugees delegation postponed their trip to Khyber due to perceived threats prompted by a warning from Pakistan’s Ministry of Interior.
Meanwhile, the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan (IEA) has repeatedly rejected such allegations made by Pakistan government, and said that Afghanistan is not responsible for the ‘security failure’ of Islamabad.
“These are false and repeated claims. We must mention that we have a position that Afghanistan’s soil will not be used against any other country, including Pakistan, and that Pakistan should understand and prevent its own problems in its own soil. Afghanistan is not responsible for the attacks in Pakistan,” IEA’s spokesman Zabihullah Mujahid said.
Latest News
Eight Afghan migrants die as boat capsizes off Greek island
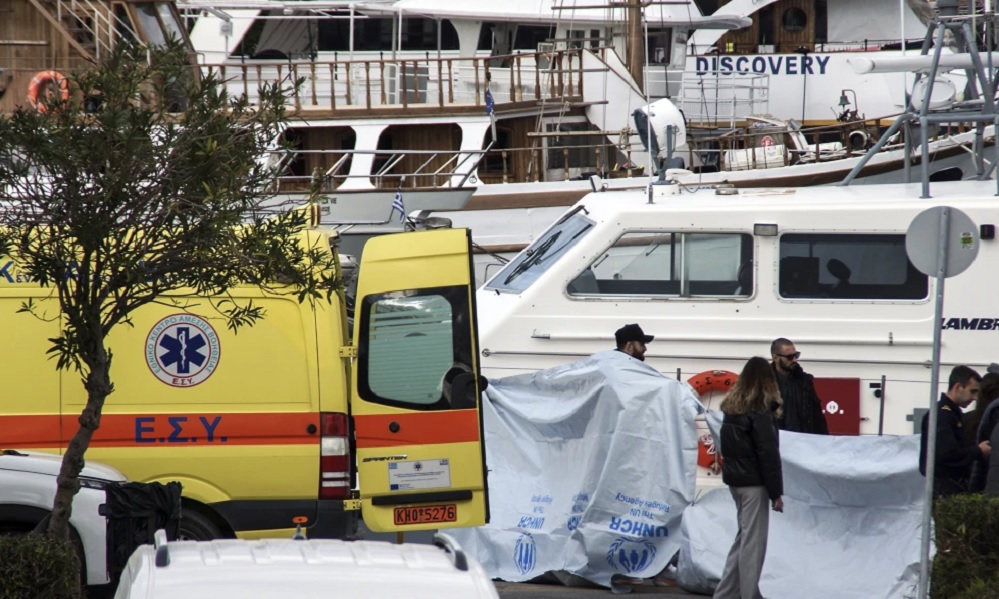

Eight Afghan migrants died after a speedboat carrying migrants capsized off Greece's eastern island of Rhodes on Friday, the Associated Press reported.
Greek authorities said that the capsizing was the result of the boat’s maneuvering to evade a patrol vessel.
A total of 18 migrants — 12 men, three women and three minors — all Afghan nationals, were rescued, Greece's coast guard said Saturday. The dead were also from Afghanistan, it said.
Some migrants remained hospitalized, with one in critical condition, authorities said.
Two Turkish citizens, ages 23 and 19, were arrested as the suspected traffickers. The boat sank after capsizing, the coast guard said.
The sinking off Rhodes was the second deadly incident involving migrants in the past week.
Seven migrants were killed and dozens were believed missing after a boat partially sank south of the island of Crete over the weekend — one of four rescue operations during which more than 200 migrants were rescued.
Latest News
Norwegian Chargé d’Affaires meets with IEA deputy foreign minister
Welcoming the diplomat’s visit to Kabul, Stanikzai underscored the importance of political relations between Afghanistan and Norway, the foreign ministry said in a statement.
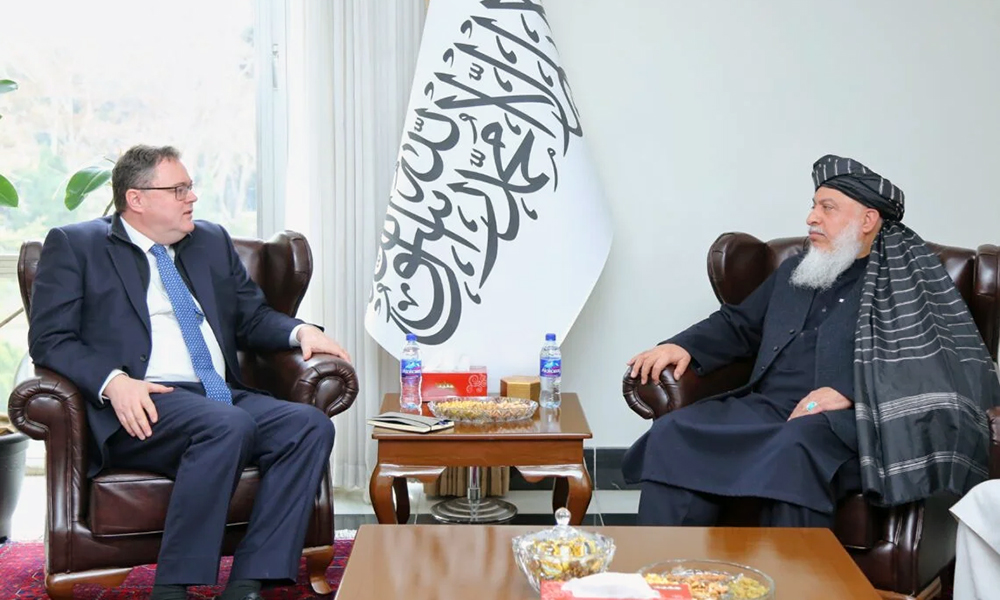

The Norwegian Chargé d’Affaires for Afghanistan, Per Albert Ilsaas, on Saturday met with IEA’s Deputy Foreign Minister for Political Affairs, Sher Muhammad Abbas Stanikzai, in Kabul.
Welcoming the diplomat’s visit to Kabul, Stanikzai underscored the importance of political relations between Afghanistan and Norway, the foreign ministry said in a statement.
In addition to focusing on bilateral political, humanitarian, and other pertinent issues, the two sides expressed hope that continued engagement would lead to constructive solutions to related issues.
This comes two weeks after the Foreign Ministry Spokesman Abdul Qahar Balkhi expressed disappointment regarding the decision by the Norwegian government to downgrade diplomatic relations with Afghanistan.
Balkhi said in a post on X that such decisions should not be linked with internal affairs of other countries.
“Diplomatic engagement is most effective when it fosters mutual understanding and respect, even amidst differing viewpoints,” he stated.
“Access to consular services is a fundamental right of all nationals. We strongly urge all parties to prioritize this principle in the spirit of international cooperation,” he added.
Latest News
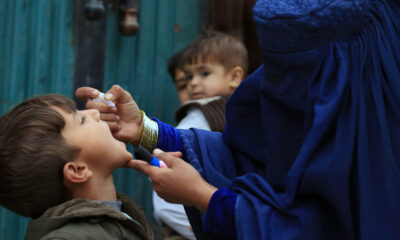
A new polio vaccination campaign is set to launch in Afghanistan
Afghanistan and Pakistan are the only two countries in the world where polio has not been eradicated.
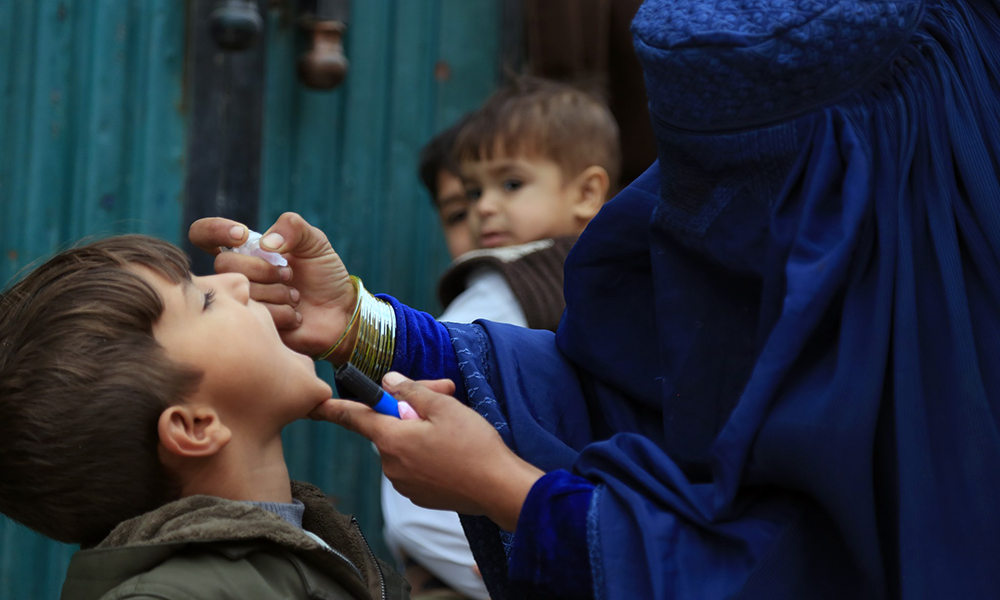
The “Afghanistan Polio-Free” organization announced that a new round of polio vaccinations will begin on Monday, December 23, in various provinces of Afghanistan.
The organization did not specify which provinces will be targeted or how long the vaccination campaign will last.
Afghanistan and Pakistan are the only two countries in the world where polio has not been eradicated.
On December 4, 2023, the World Health Organization (WHO) issued a statement reporting a 283% increase in polio cases in Afghanistan. According to the WHO, the number of positive environmental samples for wild poliovirus type 1 in Afghanistan in 2024 reached 84, compared to 62 cases in 2023.
The Ministry of Public Health claimed in November 2024 that no new cases of polio had been reported in Afghanistan for the year.
-

 Sport4 days ago
Sport4 days agoZimbabwe’s opening ODI against Afghanistan abandoned
-

 World3 days ago
World3 days agoNorth Korean troops suffer 100 deaths, struggling in drone warfare, South Korea says
-

 Latest News3 days ago
Latest News3 days agoTwo horror accidents on Kabul-Kandahar highway leave 52 dead
-

 Latest News1 day ago
Latest News1 day agoAfghan men must stand with women to support viable future of country: US envoy
-

 International Sports4 days ago
International Sports4 days agoLanka T10: Kandy Bolts in at 4th spot in playoffs after thrilling day
-

 Sport3 days ago
Sport3 days agoAfghanistan crush Zimbabwe by 232 runs in second ODI
-

 Regional4 days ago
Regional4 days agoIran’s president to make rare visit to Egypt for D-8 summit
-

 Latest News5 days ago
Latest News5 days agoKunduz families get much needed food aid, thanks to Bayat Foundation