Health
No direct evidence COVID started in Wuhan lab: US intelligence report
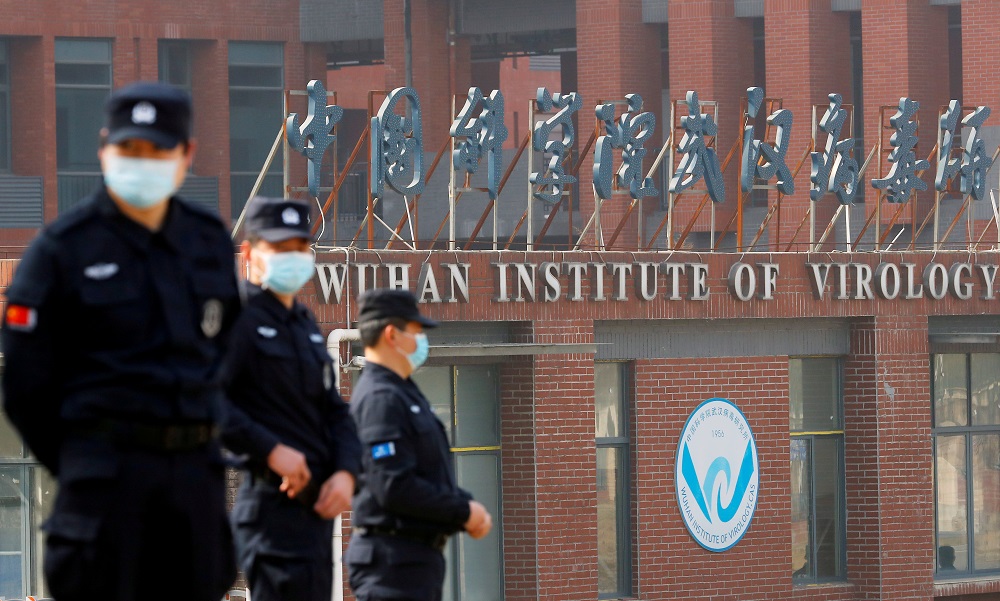

U.S. intelligence agencies found no direct evidence that the COVID-19 pandemic stemmed from an incident at China’s Wuhan Institute of Virology, a report declassified on Friday said.
The four-page report by the Office of the Director of National Intelligence (ODNI) said the U.S. intelligence community still could not rule out the possibility that the virus came from a laboratory, however, and had not been able to discover the origins of the pandemic, Reuters reported.
“The Central Intelligence Agency and another agency remain unable to determine the precise origin of the COVID-19 pandemic, as both (natural and lab) hypotheses rely on significant assumptions or face challenges with conflicting reporting,” the ODNI report said.
The report said that while “extensive work” had been conducted on coronaviruses at the Wuhan institute (WIV), the agencies had not found evidence of a specific incident that could have caused the outbreak.
“We continue to have no indication that the WIV’s pre-pandemic research holdings included SARSCoV-2 or a close progenitor, nor any direct evidence that a specific research-related incident occurred involving WIV personnel before the pandemic that could have caused the COVID pandemic,” the report said.
The origins of the coronavirus pandemic have been a matter of furious debate in the United States almost since the first human cases were reported in Wuhan in late 2019.
U.S. President Joe Biden in March signed a bill declassifying information related to the origins of the pandemic.
Biden said at the time of signing that he shared Congress’ goal of releasing as much information as possible about the origin of COVID-19.
The debate was refueled by a Wall Street Journal report in February that the U.S. Energy Department had assessed with “low confidence” in a classified intelligence report that the pandemic most likely arose from a Chinese laboratory leak, an assessment Beijing denies.
FBI director Christopher Wray said on Feb. 28 his agency had assessed for some time that the origins of the pandemic were “most likely a potential lab incident” in the Chinese city of Wuhan. China said this claim had “no credibility whatsoever”.
As of March 20, four other U.S. agencies still judged that COVID-19 was likely the result of natural transmission, while two were undecided.
Health
Health ministry holds meeting with envoys of international organizations in Kabul
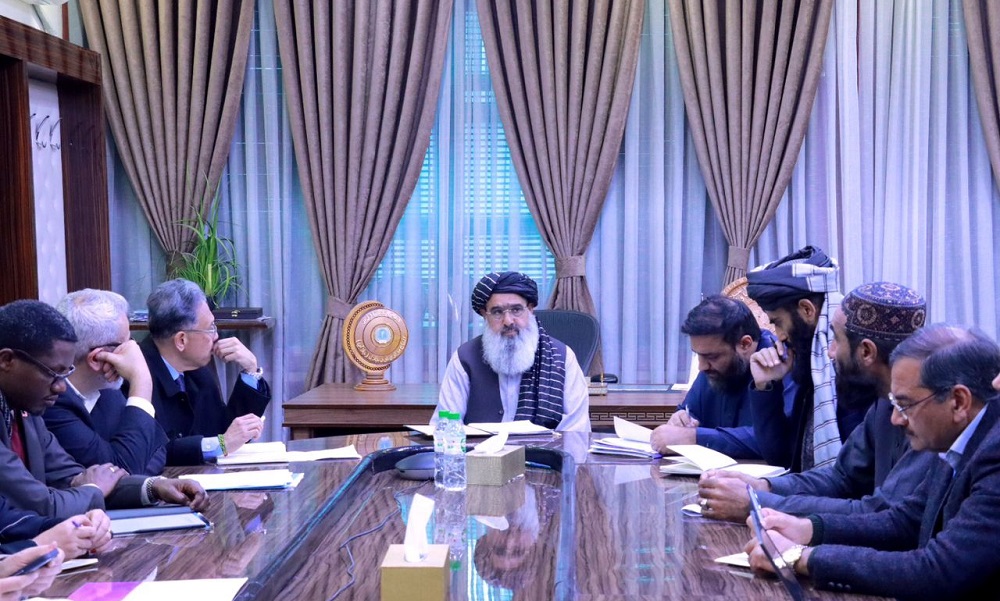

Noor Jalal Jalali, Minister of Public Health of Afghanistan, held a meeting in Kabul with representatives of the World Health Organization, UNICEF, the World Bank, the Asian Development Bank, the European Union, the UK Foreign, Commonwealth and Development Office (FCDO), and other international organizations.
According to the ministry’s statement, representatives of these international organizations discussed the delivery of health and development services, improving the management of aid and resources in the health sector, integrating health facilities and aligning them with the new policy, providing health services in accordance with the Ministry of Public Health’s policy, strengthening the immunization and vaccination sector, delivering services based on priorities, and ensuring sustained coordination.
During the meeting, Jalali stressed the need for transparency and attention to the ministry’s priorities in order to enhance the effectiveness and impact of health services. He added that the delivery of health services must be carried out in line with the ministry’s policy and through better management of existing international assistance.
Referring to vaccination campaigns, he stated that the recent measles and polio vaccination campaign had been implemented very successfully, and emphasized that necessary preparations should be made for upcoming campaigns.
He also provided information regarding the review of the BPHS and EPHS health packages and the establishment of a standardized system through technical committees.
In this meeting, Edwin Ceniza, the WHO Representative for Afghanistan, reaffirmed the organization’s continued cooperation with the Ministry of Public Health and expressed appreciation to the ministry’s leadership for their tireless efforts to improve the health system.
Representatives of these organizations pledged to maintain effective and sustained coordination and to provide their services within the country in accordance with the policies and principles of the Ministry of Public Health.
Health
IEA health delegation travels to Turkey
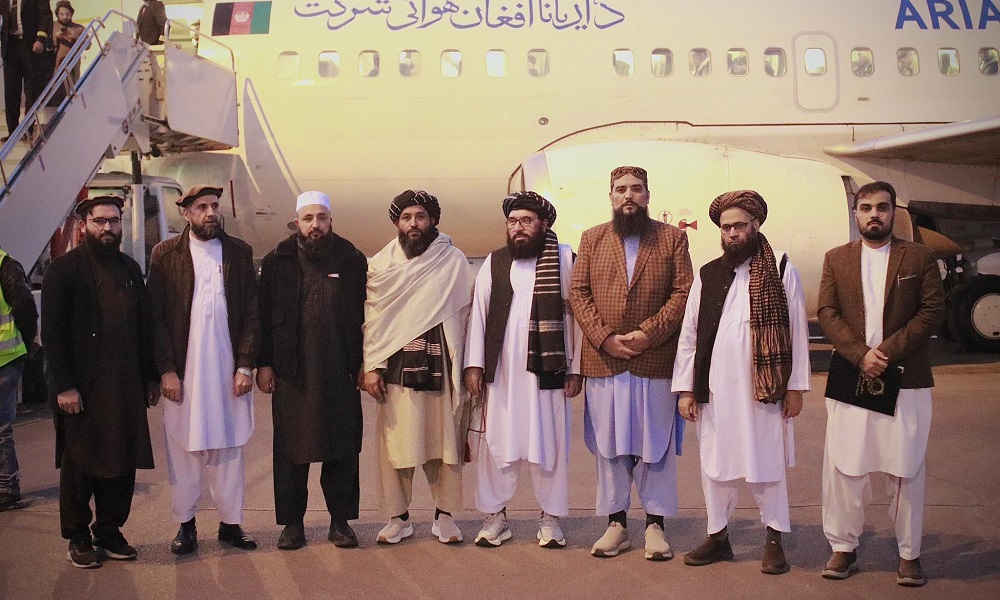

Abdul Wali Haqqani, Deputy Minister for Health Services at the Ministry of Public Health of the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan (IEA), has departed for Turkey on an official visit accompanied by a high-ranking delegation.
According to a statement released by the Health Ministry on Wednesday, the trip aims to acquire new health-sector expertise, assess Turkish medical and scientific institutions, meet with Turkish health and government officials, and strengthen bilateral cooperation.
During the visit, the delegation is scheduled to meet representatives from both public and private health sectors to support improvements in Afghanistan’s healthcare system and enhance coordination between the two countries, the statement added.
Health
Polio vaccination drive launches across 17 Afghan provinces
Officials say routine vaccination remains the most effective tool for eliminating polio and have urged families to fully cooperate with health teams during the campaign.
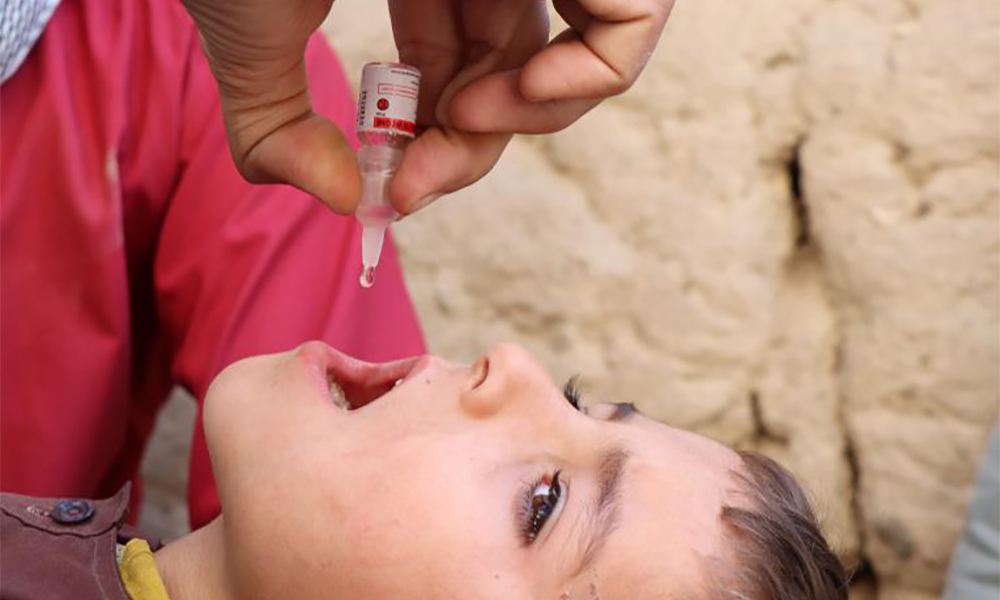
The Ministry of Public Health has announced the launch of a major anti-polio vaccination campaign, set to begin on Monday across 17 provinces of Afghanistan.
According to Sharafat Zaman, spokesperson for the ministry, the nationwide initiative will target 7.4 million children under the age of five, delivering vaccines door-to-door to prevent the spread of the poliovirus and safeguard children’s health.
Officials say routine vaccination remains the most effective tool for eliminating polio and have urged families to fully cooperate with health teams during the campaign.
This effort forms part of the government’s ongoing strategy to protect Afghanistan’s next generation from preventable diseases and strengthen public health across the country.
This comes after the World Health Organization (WHO) recently again classified the global spread of poliovirus as a Public Health Emergency of International Concern (PHEIC), warning that the disease remains endemic in only two countries — Afghanistan and Pakistan.
The decision followed the 43rd meeting of the Polio Emergency Committee under the International Health Regulations (IHR), which convened on 1 October 2025.
According to the Committee, Afghanistan reported four new wild poliovirus type 1 (WPV1) cases so far this year, compared to 24 in Pakistan.
The Afghan cases were detected in the country’s southern and eastern regions, where transmission remains intense despite ongoing vaccination efforts.
-

 Latest News2 days ago
Latest News2 days agoMuttaqi: Afghanistan’s progress requires both religious and modern education
-

 Sport4 days ago
Sport4 days agoILT20: Desert Vipers edge Gulf Giants in historic super over thriller
-

 Regional4 days ago
Regional4 days agoSix Pakistani soldiers killed in TTP attack in Kurram District
-

 Business4 days ago
Business4 days agoTrade bodies warn almost 11,000 Afghan transit containers stuck at Karachi port
-

 World4 days ago
World4 days agoPowerful 7.6 earthquake hits northern Japan, tsunami warnings issued
-

 Latest News3 days ago
Latest News3 days agoTrump calls Afghanistan a ‘hellhole’ country as US expands immigration restrictions
-

 Sport5 days ago
Sport5 days agoSorkh Poshan Khafi defeats Sarsabz Yashlar 4-0 in Afghanistan Champions League
-

 Sport3 days ago
Sport3 days agoCommanding wins for Arman FC and Sarsabz Yashlar in Afghanistan Champions League
























