Business
Minerals have become integral to conflict in Afghanistan: UNDP
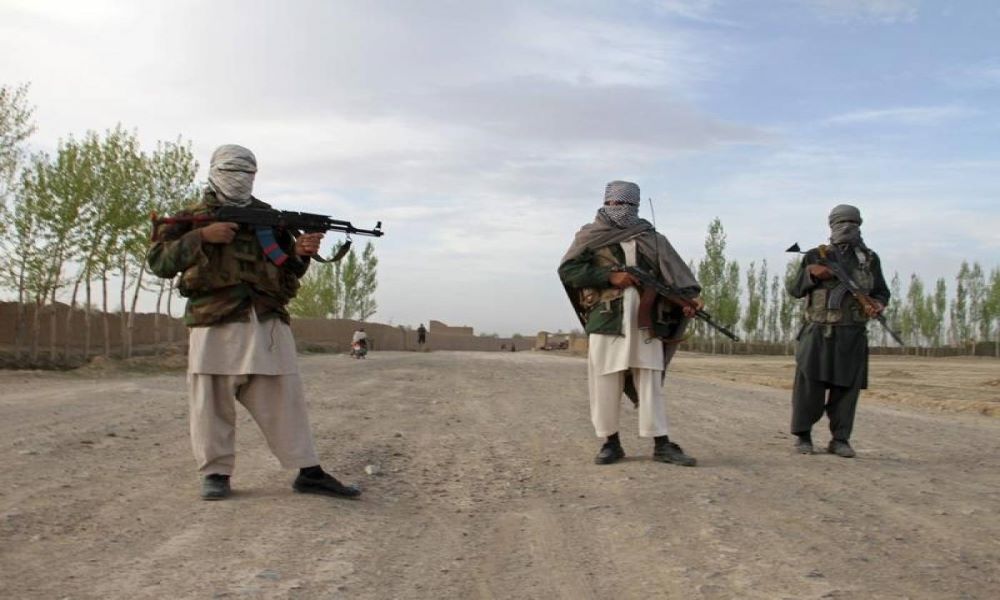

UNDP Afghanistan has found that decades of mining without a clear vision has done little to reduce poverty but has instead helped insurgent groups fund their wars, triggered local conflicts and harmed the environment.
Published on Tuesday, the UNDP’s National Human Development Report 2020 on minerals extraction in Afghanistan states that the country’s minerals extraction is poorly regulated, often illegal, and in many parts of the country is controlled by political elites, and by insurgents.
Based on extensive fieldwork, consultations and discussion, UNDP also found that illegal mining is a complex phenomenon, contributing to insecurity, corruption, human rights violations and conflict that affects the lives of citizens.
Afghanistan is richly endowed with mineral and hydrocarbon resources, which include base and precious metals, precious and semi-precious stones, rare earth elements, mineral rocks and industrial minerals, and energy resources.
At present these contribute little to the economy or society, mainly because they remain in the ground, but also because most of the mining is informal and illegal.
“If the country is to unlock the potential of its mineral wealth, the government and other stakeholders will need to strengthen the management of resources and ensure peace and security,” UNDP stated.
“Unregulated mining feeds and is fed by conflict. It has become the magnet of corrupt individuals and networks, and some mining businesses are implicated in serious human rights violations, often acting with impunity,” read the report.
“In Afghanistan, there is an urgent need to improve governance, tackle corruption and put an end to illegal extraction and trade of minerals,” said Abdallah Al Dardari, UNDP Resident Representative for Afghanistan.
“Large-scale mineral, oil and gas projects can be instrumental for financing development, but it will require stability and enhanced government capacity to get its due share from these projects and use them well for human development,” he added.
The report recommends that all partners implement programs demonstrating good practices, methods and technologies in mining.
Afghanistan’s Minister of Mines and Petroleum Haroon Chankhansuri meanwhile said: “I welcome the release of the report and look forward to our collaboration with UNDP and other partners on the opportunities explored by this report on the potential of economic growth through extractive industries.”
The minister added, “the recommendations on policy choices to ensure people benefit from and participate in extractive industries potential, and mitigating the risks associated with this type of development will be considered in the government’s plans for the sector.”
According to UNDP, the organization’s new programs, Afghanistan Sustainable Development Goals (A-SDGs) and Agenda 2030 is focused on transferring the war economy into a peace economy, and that the extractive sector is a key area for revenue generation and economic growth.
In 2010 the US Task Force for Business and Stability Operations estimated the monetary value of Afghanistan’s mineral resources at nearly $1 trillion.
But, according to the UNDP, since the 1980s, many mines have come to be controlled by networks of former jihadis who, after the defeat of the Taliban, have at different times acquired positions of influence within the government.
These networks often operate with impunity – openly and audaciously smuggling mineral resources out of the country, read the report.
“More recently, with the decline in international aid, and the reduced demand for new buildings, many well-connected construction companies have moved into the mining sector.”
Mining financing conflict
The report also stated mining has been financing conflict and that the control of minerals extraction by insurgent groups has meant that they have been financing and fuelling conflict while undermining the legitimacy of the Afghan government and further spreading corruption and violence.
“The group with the most extensive reach is the Taliban, but since 2015, other groups under the name of Islamic State of Khorasan (IS-K/Daesh) have joined the competition for minerals,” read the report.
For the Taliban, the extractive industry is the second-largest revenue stream after narcotics.
It collects taxes and ‘protection money’ from miners but more recently, the IS-K started tapping the mining sector when financial support waned from the central ISIS branch, the report stated.
One example cited was with talc-rich Nangarhar province where government, Taliban and IS-K actively contested the talc mining areas.
“For a mining company, the benefits of paying taxes to the government are limited, while the risks of not paying taxes to insurgents are enormous,” the UNDP stated adding that IS-K, in particular, is known for brutal sanctions for non-compliance.
“In addition to these groups, local militias, warlords, and occasionally security forces, are also levying taxes on minerals or are involved in illegal mineral extraction – directly or through associates and family members,” the report stated.
The UNDP stated that in areas controlled by insurgents, lucrative large-scale mining sites operate on an industrial scale then openly transport bulk minerals on large trucks along major roads and across the border to Pakistan.
“Governance of extraction is weakened by extensive corruption. Even where mining companies operate legally, there can be corruption in the issue of contracts,” the report stated.
According to UNDP, violations of human rights in regard to minerals extraction was also a problem.
“There have been documented cases of human rights violations by mining companies which are protected by networks of power brokers.”
Afghanistan is one of the world’s poorest countries – held back by decades of conflict but with prospects for peace, there will be greater opportunities for investing in human development.
The UNDP stated however that this will require taking full advantage of the country’s mineral resources.
“But it will require a determined and concerted effort to reform the country’s policies and institutions governing these resources. The ultimate objective of minerals extraction in Afghanistan should be sustainable human development and improvements in people’s well-being.”
CLICK HERE for the full report
Business
Afghanistan steps in to replace Iran in supplying fruits and vegetables to Russia

Afghanistan is preparing to increase exports of fruits and vegetables to Russia following a temporary ban by Iran on food exports, Russian media reported citing Rustam Khabibullin, head of the Russian Business Center in Afghanistan.
On March 3, the Iranian government announced an indefinite suspension of all food and agricultural exports to prioritize domestic food security amid ongoing regional conflict. Goods that were previously destined for Russian retailers are now being redirected to Iranian state reserves.
In response, Afghanistan has already dispatched its first shipment of 100 tons of apples to Russia. Shipments of peppers, dried fruits, nuts, celery, zucchini, eggplant, citrus, berries, herbs, and melons are being prepared for delivery in the coming weeks. Khabibullin noted that demand from Russia is growing, and Afghan exporters aim to meet the rising requests to prevent shortages and stabilize prices for consumers.
Business
Ministry of Public Works: Railway transport operating smoothly across all ports

The Ministry of Public Works has confirmed that railway transport through Afghanistan’s four main ports is running normally, with no disruptions reported.
According to the ministry, 127,650 metric tons of goods—including oil, non-oil items, and other materials—were transported via the railway last week (27 February–3 March). Shipments by port were as follows:
- Hairatan: 88,186 tons
- Aqina: 10,769 tons
- Torkhandi: 14,123 tons
- Khaf–Herat: 14,572 tons
Exports accounted for 265 tons, mainly dried fruits and mineral stones.
The Minister of Public Works has directed port officials and provincial department heads to ensure additional support and facilities for traders transporting essential and food items during these sensitive times.
Business
Mujahid: Trade with Iran through Khaf–Herat railway operating normally
He urged national traders to refrain from unjustified price increases in order to maintain market stability.

Zabihullah Mujahid, spokesperson for the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan, has announced that commercial transportation through the Khaf–Herat railway is continuing without interruption.
According to Mujahid, all relevant departments overseeing the railway are carrying out their routine operations, and there have been no delays in the movement of commercial goods.
He confirmed that a freight train carrying commercial goods has arrived at the Rozanak station in Herat province, transporting 42 wagons of cement and two wagons of MDF boards.
Another cargo train carrying food and fuel supplies is expected to arrive later.
Mujahid also noted that, based on information from Iranian railway authorities, around 900 wagons currently in Iran are en route to Afghanistan and will enter the country as scheduled.
He urged national traders to refrain from unjustified price increases in order to maintain market stability.
-

 Latest News4 days ago
Latest News4 days agoProminent Muslim scholar issues fatwa calling for Afghanistan-Pakistan ceasefire
-

 Business3 days ago
Business3 days agoAfghanistan steps in to replace Iran in supplying fruits and vegetables to Russia
-

 Latest News2 days ago
Latest News2 days agoAfghanistan’s Virtue Ministry: Over 3,400 women’s rights complaints addressed in 10 months
-

 Latest News3 days ago
Latest News3 days agoInternational Women’s Day: Khalilzad urges IEA to allow girls’ education
-

 Latest News4 days ago
Latest News4 days agoAfghanistan says 327 Pakistani soldiers killed in ‘Radd-ul-Zulm’ operation
-
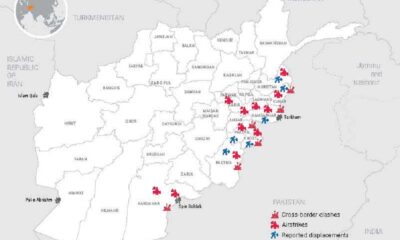
 Latest News4 days ago
Latest News4 days agoAirstrikes and clashes displace thousands as Afghanistan–Pakistan tensions escalate: UN
-

 Latest News3 days ago
Latest News3 days agoAfghans among those injured in Iranian attacks on UAE
-

 World5 days ago
World5 days agoTrump wants say on Iran’s next leader as war intensifies
























