Health
Malaria remains a public health concern in Afghanistan
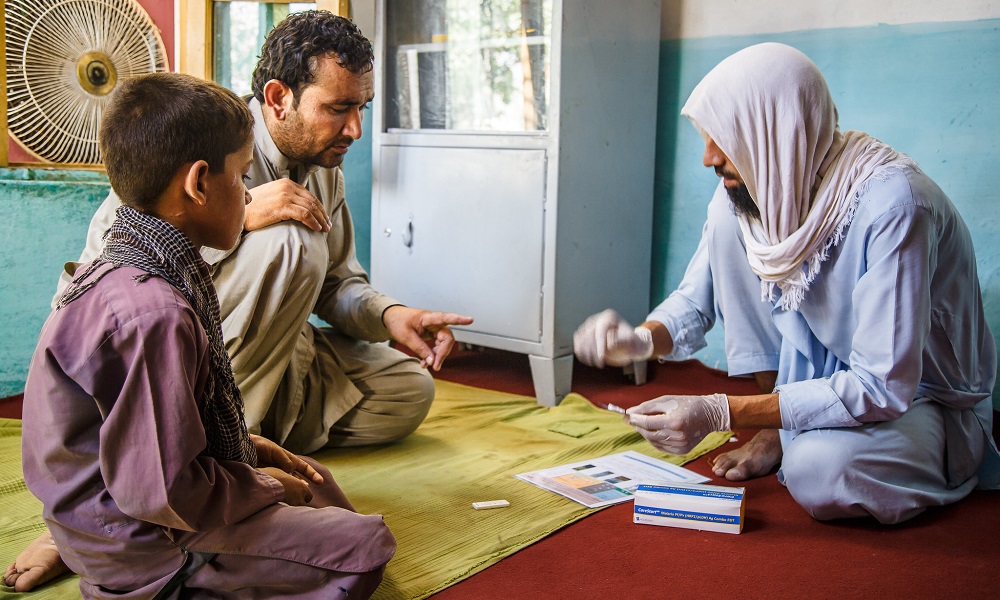

The United Nations Development Program (UNDP) has reported that malaria remains a public health concern as 27% of Afghans live in areas where there is a high risk of the disease.
According to UNDP, 50% of the people in Afghanistan live in areas where the probability of contracting malaria is moderate, and only 23% of them live in areas where the risk of contracting malaria is low or does not exist.
This organization said the transmission of this disease, which is more prevalent in summer, varies from one region to another for several reasons.
According to their report, the confirmed number of malaria cases dropped from more than 391,000 cases in 2012 to 175,000 in 2019.
The World Health Organization meanwhile reports that globally 249 million cases were recorded in 2022, across 85 countries. The death toll was 608,000.
Malaria is a serious and sometimes fatal disease caused by a parasite that commonly infects a certain type of mosquito which feeds on humans. People who get malaria are typically very sick with high fevers, shaking chills, and flu-like illness.
The disease is however preventable and curable.
Health
Head of MSF in Afghanistan meets with Jalali over improving healthcare services
Michael Lippi committed to making efforts aimed at improving the quality of healthcare services and fostering better coordination.

Afghanistan’s Acting Minister of Health Noorjilal Jalali met with the head of Medecins Sans Frontieres (MSF) for Afghanistan, Michael Lippi, for discussions on improving healthcare centers and medical services in the country.
The two officials also discussed enhancing the capacity of healthcare workers, ensuring transparency in services, improving coordination with the Ministry of Public Health, and delivering effective and sustainable healthcare services.
Jalali emphasized the importance of increasing and expanding the organization’s support for the health sector and called for further development of services.
He stressed the need to enhance the capacity, quality, effectiveness, and transparency of healthcare workers.
Michael Lippi also emphasized the need for further improvements in health services in Afghanistan and the expansion of this sector.
He committed to efforts aimed at improving the quality of healthcare services and fostering better coordination. He specifically addressed the continuation of services in the provinces of Herat, Kunduz, and Helmand, confirming that these centers will continue their operations in collaboration with the Ministry of Public Health.
Meanwhile, Mohammad Naeem, the Deputy Minister for Finance and Administration at the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of the Interim Government, held a separate meeting with
Michael Lippi to discuss the expansion of healthcare services and the provision of necessary facilities for returning migrants.
According to the Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Lippi reassured government that MSF’s efforts to improve maternal and child health and enhance the capacity of healthcare personnel will continue.
Health
Japanese charity Peshawar-Kai to resume leprosy treatment in Afghanistan
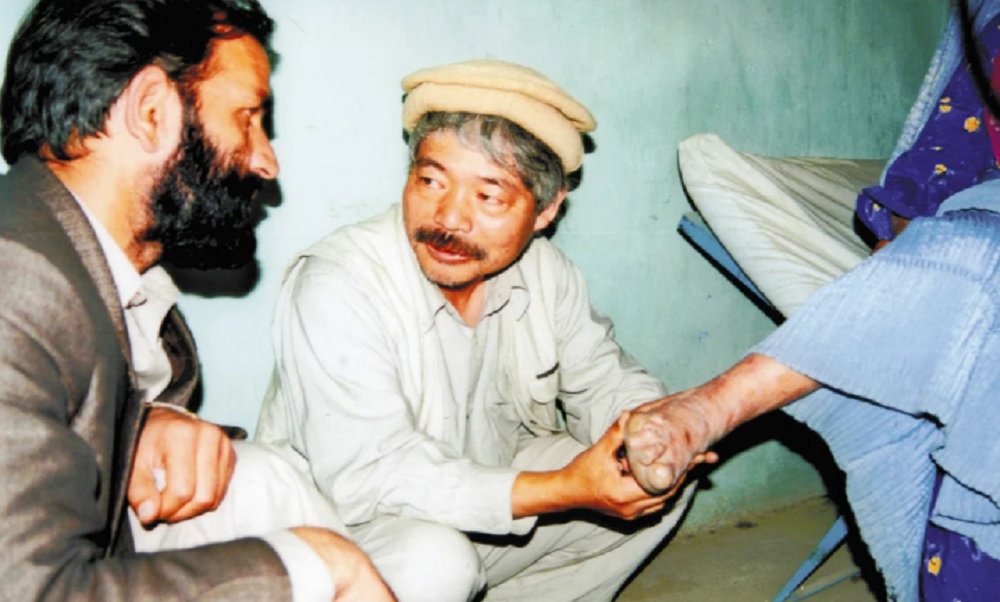
Peshawar-Kai, a Japanese aid organization, has announced that it will resume leprosy treatment in Afghanistan after around 15 years.
The charity will treat leprosy patients in memory of its former head Tetsu Nakamura, Japan’s Yomiuri Shimbun newspaper reported.
The NGO will begin its leprosy treatment program in Afghanistan this year.
It will treat patients in areas such as Nangarhar province by providing medicines, training staff and sending mobile treatment teams.
Leprosy, also known as Hansen disease, is a chronic infectious disease caused mainly by a type of bacteria called Mycobacterium leprae. The disease affects the skin, the peripheral nerves, the mucosa of the upper respiratory tract and the eyes.
Nakamura started treated leprosy patients in Pakistan in the 1980s and then began extensive activities, including the construction of water supply canals in Afghanistan.
The Japanese aid worker was killed in an armed attack in Jalalabad in December 2019.
Health
WHO confirms second Polio case in Afghanistan
The Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan’s Public Health Ministry has not yet commented.
The World Health Organization (WHO) has confirmed the second case of polio in Afghanistan for the year 2025.
The case was identified in March in Helmand province.
This follows the first reported case in the Bala Murghab district of Badghis province, where a five-year-old girl was diagnosed with the virus.
Additionally, 18 environmental samples testing positive for the polio virus have been reported in provinces including Kandahar, Helmand, Kabul, Laghman, Nangarhar, and Zabul.
Afghanistan and Pakistan remain the only countries where polio has not been eradicated.
Polio is a viral disease for which there is no cure, and vaccination is the only way to protect children from it.
The Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan’s Public Health Ministry has not yet commented.
-
 Health5 days ago
Health5 days agoJapanese charity Peshawar-Kai to resume leprosy treatment in Afghanistan
-

 Latest News5 days ago
Latest News5 days agoEx-Afghan deputy speaker Qadeer back in Kenyan court for criminal case
-

 Sport5 days ago
Sport5 days agoIndia suspends Indian Premier League T20 cricket tournament
-

 Latest News4 days ago
Latest News4 days agoPakistan says India launched attack on Afghanistan, India denies
-

 Latest News5 days ago
Latest News5 days agoMCC Chief: Afghan cadres sent to China for AI training
-

 World4 days ago
World4 days agoUS offers to help India and Pakistan start talks, G7 also urges dialogue
-

 Sport4 days ago
Sport4 days agoFIFA OKs creation of Afghanistan women’s refugee team
-

 Regional4 days ago
Regional4 days agoPakistan says it has launched military offensive against India
























