Health
Long working hours are a killer: WHO study shows
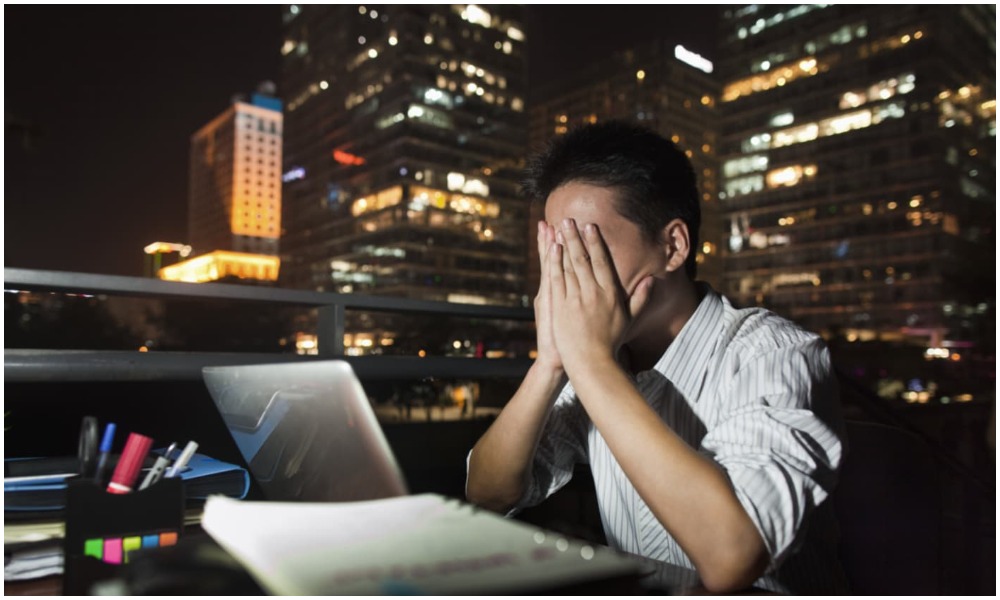

Working long hours is killing hundreds of thousands of people a year in a worsening trend that may accelerate further due to the COVID-19 pandemic, the World Health Organization said on Monday.
In the first global study of the loss of life associated with longer working hours, the paper in the journal Environment International showed that 745,000 people died from stroke and heart disease associated with long working hours in 2016, Reuters reported.
That was an increase of nearly 30% from 2000.
“Working 55 hours or more per week is a serious health hazard,” said Maria Neira, director of the WHO’s Department of Environment, Climate Change and Health.
“What we want to do with this information is promote more action, more protection of workers,” she said.
The joint study, produced by the WHO and the International Labour Organization, showed that most victims (72%) were men and were middle-aged or older. Often, the deaths occurred much later in life, sometimes decades later, than the shifts worked.
It also showed that people living in Southeast Asia and the Western Pacific region — a WHO-defined region which includes China, Japan and Australia — were the most affected, Reuters reported.
Overall, the study – drawing on data from 194 countries – said that working 55 hours or more a week is associated with a 35% higher risk of stroke and a 17% higher risk of dying from ischemic heart disease compared with a 35-40 hour working week.
The study covered the period 2000-2016, and so did not include the COVID-19 pandemic, but WHO officials said the surge in remote working and the global economic slowdown resulting from the coronavirus emergency may have increased the risks.
“The pandemic is accelerating developments that could feed the trend towards increased working time,” the WHO said, estimating that at least 9% of people work long hours.
WHO staff, including its chief Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus, say they have been working long hours during the pandemic and Neira said the U.N. agency would seek to improve its policy in light of the study, Reuters reported.
Capping hours would be beneficial for employers since that has been shown to increase worker productivity, WHO technical officer Frank Pega said.
“It’s really a smart choice not to increase long working hours in an economic crisis.”
Health
Aid cuts could leave more women dying in pregnancy and birth, UN says
The cuts have had “pandemic-like effects” on health systems globally and could have a “more structural, deep-seated effect”, says WHO director
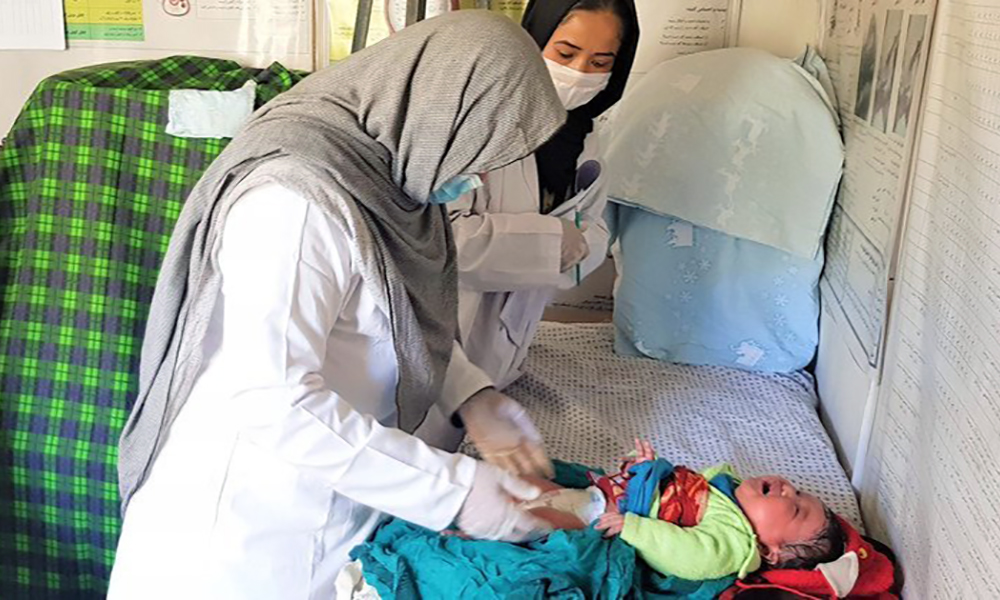

Cuts to aid budgets are threatening to undermine years of progress in reducing the number of women dying during pregnancy and childbirth, and could lead to a rise in deaths, the United Nations has warned.
Globally, there was a 40% decline in maternal deaths between 2000 and 2023, a report by UN agencies including the World Health Organization (WHO) showed on Monday, largely due to better access to essential health services.
That could now go into reverse, the WHO said in a statement accompanying the report which did not mention specific cuts but came in the wake of a foreign aid freeze by the U.S. government and the ending of funding through the United States Agency for International Development (USAID) for many programmes.
Other donor countries including Britain have also announced plans to cut aid budgets.
“One of the headline messages is that the funding cuts risk not only that progress, but we could have a shift backward,” said Dr Bruce Aylward, Assistant Director-General, Universal Health Coverage at the WHO.
The cuts have had “pandemic-like effects” on health systems globally and could have a “more structural, deep-seated effect,” Aylward added.
The WHO said the cuts were already rolling back vital services for maternal, newborn and child health in many countries, reducing staff numbers, closing facilities and disrupting supply chains for supplies including treatments for hemorrhage and pre-eclampsia.
Cuts to other areas, such as malaria and HIV treatment, would also impact maternal survival, the UN said.
Even before the aid cuts led by the United States, things were backsliding in some countries, and progress has slowed globally since 2016, the report said.
In 2023, despite recent progress, a woman still died roughly every two minutes – around 260,000 in total that year – from complications that were mainly preventable and treatable, it added.
The situation was particularly bad in countries affected by conflict or natural disaster, although the U.S. itself is one of only four countries to have seen its maternal mortality rate increase significantly since 2000, alongside Venezuela, the Dominican Republic and Jamaica.
The COVID-19 pandemic also had an impact, the report said: 40,000 more women died due to pregnancy or childbirth in 2021, bringing the total number of deaths that year to 322,000.
“While this report shows glimmers of hope, the data also highlights how dangerous pregnancy still is in much of the world today – despite the fact that solutions exist,” WHO Director-General Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus said.
Health
Global organizations warn of health crisis due to aid cuts in Afghanistan
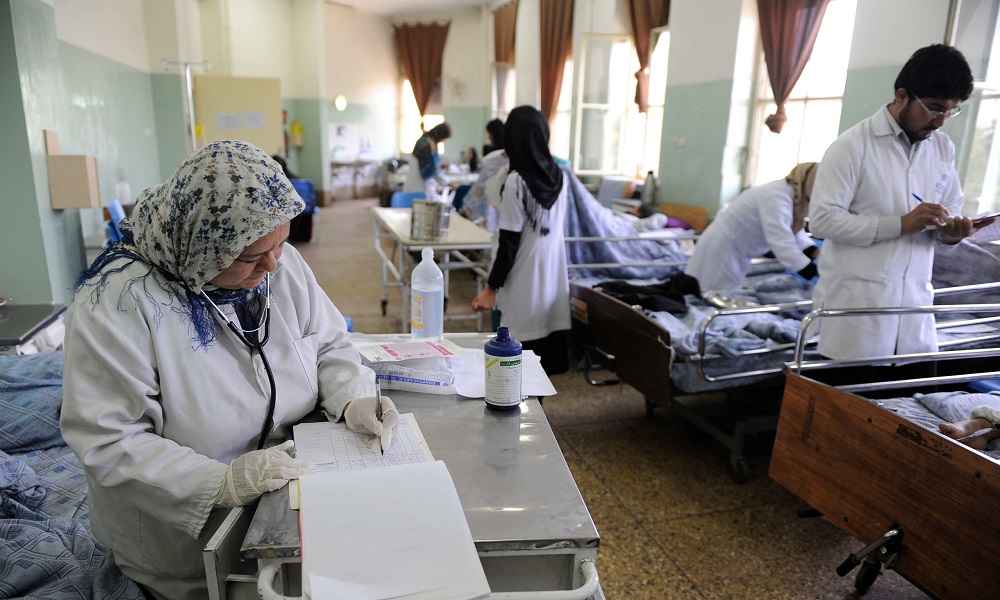

Global organizations are raising alarms about the impact of aid cuts on Afghanistan’s health sector and the reduction in funding for humanitarian organizations operating in the country.
UN-affiliated bodies have stated that the complete suspension of aid from the United States and the reduction of the 2025 budget could lead to the closure or suspension of nearly 2,000 healthcare centers across Afghanistan.
The United Nations Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs (OCHA) has further warned that if only 25 percent of the required funding is provided, 7 million out of the 9.3 million people in need of medical services will be left without access to healthcare.
The report highlights that without immediate and sufficient funding, child mortality rates could rise sharply, as malnutrition remains one of the leading causes of death for children under the age of five.
The World Food Programme (WFP) has also warned that Afghanistan is facing a severe malnutrition crisis among children, with the number of malnourished children expected to reach 3.5 million by 2025.
Recent reports from the WFP reveal that 8 out of 10 families in Afghanistan are unable to afford a sufficient diet, and 3 out of 4 families are being forced to borrow money to purchase basic food items.
UN agencies have stressed the urgent need for the international community to address the humanitarian crisis in Afghanistan and provide the necessary aid.
This comes after Afghanistan’s Ministry of Economy dismissed reports from some international organizations about the growing poverty in the country, labeling them as exaggerated and far from reality.
Health
Health minister meets with Qatari envoy over building of 400-bed hospital in Kandahar
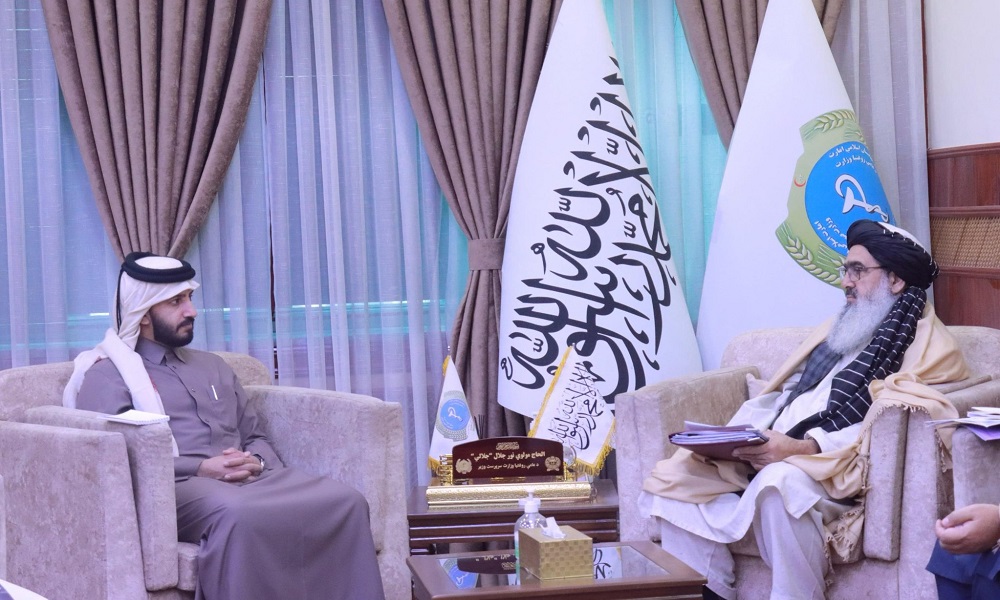

The Ministry of Public Health has announced that Noor Jalal Jalali, the acting public health minister, met with Murdif Al-Qashouti, the Chargé d’Affaires of the Qatari Embassy in Kabul, to discuss the construction of a planned 400-bed hospital by Qatar, the provision of equipment for hospitals, and the enhancement of the capacity of health workers in Kandahar province.
According to a statement, the Acting Minister of Public Health emphasized the importance of improving the capacity of health workers and equipping hospitals with standard facilities to better address patients’ needs and provide essential health services. He considers Qatar’s cooperation to be crucial.
In this meeting, Al-Qashouti assured the IEA of Qatar’s commitment to supporting various health sectors in Afghanistan.
In November 2023, the Ministry of Public Health had announced that Qatar planned to build a 400-bed hospital in Kandahar. In September 2023, reports also emerged about Qatar Charity’s commitment to constructing this hospital.
However, Qatar has not yet started the actual construction of the hospital.
International organizations have repeatedly warned that attention must be given to Afghanistan’s health system, as the country cannot effectively manage patients and combat infectious diseases such as polio and tuberculosis without the support of global organizations.
-

 Latest News4 days ago
Latest News4 days agoUN rights experts call on Pakistan to stop removal process of Afghan refugees
-

 Science & Technology4 days ago
Science & Technology4 days agoMeta releases new AI model Llama 4
-

 Latest News3 days ago
Latest News3 days agoIEA rejects reports of US military planes landing at Afghanistan’s Bagram Air Base
-

 Latest News5 days ago
Latest News5 days agoPakistan urges global community to block arms flow to militant groups in Afghanistan
-

 Sport4 days ago
Sport4 days agoAfghanistan Under-19s beat Nepal by 1 run in second ODI, win series
-

 World4 days ago
World4 days agoAnti-Trump protesters gather in Washington, other US cities
-

 Regional4 days ago
Regional4 days agoRains add to challenge for Myanmar quake relief, toll at 3,471
-

 Latest News3 days ago
Latest News3 days agoTrump’s tariff pressure on Afghanistan ‘will impact economic growth’