Regional
India’s Modi set for a record third term, but with much smaller majority
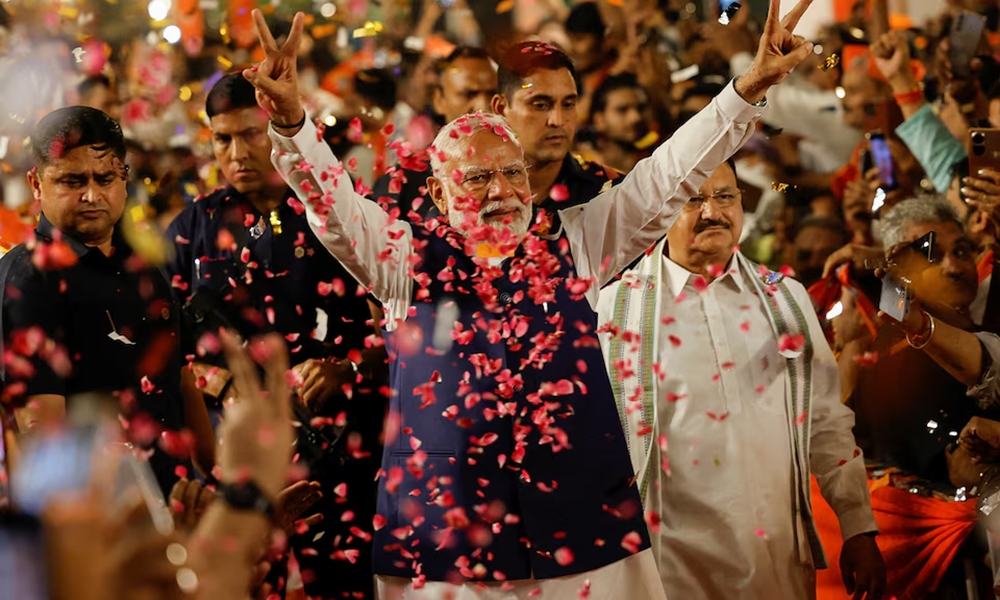
Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi was set for a historic third term on Tuesday, but with a vastly diminished majority in a rare electoral setback for a leader who has held a tight grip on the nation’s politics, Reuters reported.
Modi’s ruling Bharatiya Janata Party lost its own majority in parliament for the first time in a decade and is dependent on its regional allies to get past the half-way mark required to run the world’s largest democracy.
For Modi whose approval ratings have been the highest among world leaders and who ran a presidential-style campaign, such a result is the first sign of the ground shifting.
“For the BJP to drop below the majority mark, this is a personal setback for him,” said Yogendra Yadav, a psephologist and the founder of a small political group opposed to the BJP.
Since he took power 10 years ago, riding his Hindu nationalist base, Modi has been the ruling alliance’s unquestioned leader, with concerns growing about what his opponents see as the country’s slide towards authoritarianism, read the report.
The man who as a boy sold tea in his home state of Gujarat has dominated India’s politics so completely in the last decade that few in his party or even the parent ideological group, the Rashtriya Swayamsevak Sangh, dare stand up to him.
Indeed, throughout the campaign in scorching heat, it was Modi with his thinning white hair, a neatly trimmed white beard and immaculate Indian attire who towered over everyone else.
His giant cutouts were everywhere, his face on television screens every day as he courted India’s 968 million voters with a personal “Modi guarantee” to change their lives.
“My sole issue with Modi today is that he has become larger than the party itself,” said Surendra Kumar Dwivedi, a former head of the Department of Political Science at Lucknow University “In a democratic system… a party should always supersede an individual.”
‘LAST 10 YEARS IS ONLY A PREVIEW’
Still, Modi will be only the second leader to win a third term after founding prime minister Jawaharlal Nehru and has promised a transformative next five years.
Under him, India has become the world’s fastest growing major economy and he has said he wants to make it the world’s third largest in three years, behind the United States and China.
“What we have done in the last 10 years is only a preview, a trailer,” Modi told a recent rally. “We have a lot more to do. Modi is taking the country to a different level in the world.”
The BJP has dismissed opposition speculation that Modi, 73, might hang up his boots once he reaches 75, like some other party leaders have done in recent years. Modi has said he wants to lay the groundwork for India to become a fully developed nation by 2047, the 100th year of independence from British colonial rule, read the report.
“Modi will now probably enter in what I call the legacy phase of his prime ministership, driving India forward politically, economically, diplomatically and even militarily,” said Bilveer Singh, deputy head, department of political science, at the National University of Singapore.
The idea would be to make the country a “strong regional power that is also a counterbalance to China, but not to serve Western interest as is sometimes alleged, but mainly to promote India’s interest, power and place in international politics”.
A reduced mandate for Modi’s ruling alliance forecloses the possibility of changes to India’s secular constitution that opposition groups had warned against. Any such measures require the support of two-thirds of members of parliament.
Concerns have grown in recent years that the BJP’s Hindu nationalist agenda has polarised the country with Modi himself turning up the rhetoric, accusing the main opposition Congress of appeasing Muslims for votes, Reuters reported.
Yashwant Deshmukh, founder of CVoter polling agency and a political analyst, said the BJP’s top goal of introducing common civil laws to replace Islam’s sharia-based customs and other religious codes would have to go on the back burner.
“These will have to be debated,” he said.
Regional
Iran can’t enrich uranium, could only import it for civilian program, Rubio says
Iran has denied wanting to develop a nuclear weapon and says its nuclear program is peaceful. U.S. and Iranian officials will meet in Oman on Saturday for a third round of talks.
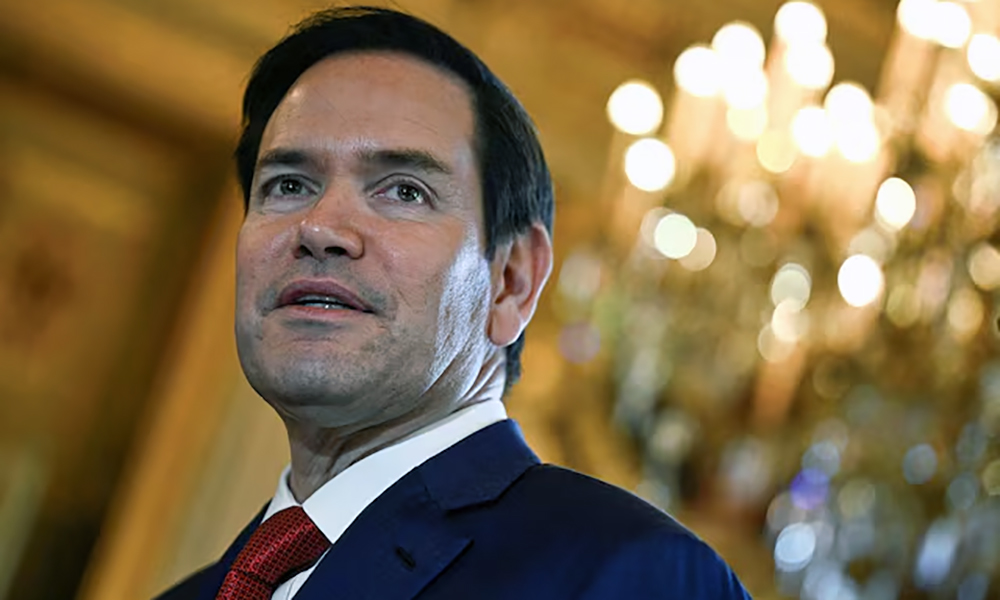

Iran will have to stop enriching uranium under any deal with the United States and could only import what is needed for a civilian nuclear program, U.S. Secretary of State Marco Rubio said ahead of talks between Tehran and Washington on Saturday, Reuters reported.
However, Iran has already made clear that its right to enrich uranium is not negotiable. When asked about Rubio’s comments, a senior Iranian official, close to Iran’s negotiating team, again said on Wednesday “zero enrichment is unacceptable.”
The U.S. is seeking to prevent Iran from developing a nuclear bomb and President Donald Trump has imposed a “maximum pressure” campaign of sanctions and threatened to use military force if Iran does not end its nuclear program.
Iran has denied wanting to develop a nuclear weapon and says its nuclear program is peaceful. U.S. and Iranian officials will meet in Oman on Saturday for a third round of talks on Tehran’s disputed nuclear program.
“There’s a pathway to a civil, peaceful nuclear program if they want one,” Rubio told the “Honestly with Bari Weiss” podcast on Tuesday.
“But if they insist on enriching, then they will be the only country in the world that doesn’t have a ‘weapons program,’ … but is enriching. And so I think that’s problematic,” he said.
U.S. Middle East envoy Steve Witkoff last week said Iran does not need to enrich past 3.67% – a remark that raised questions as to whether Washington still wanted Tehran to dismantle its enrichment program, read the report.
Witkoff then said a day later that Iran must “stop and eliminate its nuclear enrichment.”
Rubio said on Tuesday that Witkoff was initially talking about “the level of enriched material that they would be allowed to import from outside, like multiple countries around the world do for their peaceful civil nuclear programs.”
“If Iran wants a civil nuclear program, they can have one just like many other countries in the world have one, and that is they import enriched material,” he said.
The U.N. nuclear watchdog – the International Atomic Energy Agency – has said that Iran is “dramatically” accelerating enrichment of uranium to up to 60% purity, close to the roughly 90% weapons-grade level.
Western countries say there is no need to enrich uranium to such a high level for civilian uses and that no other country has done so without producing nuclear bombs.
Regional
Lavrov in Uzbekistan for talks on various issues including regional security matters
Lavrov is expected to meet with Uzbek President Shavkat Mirziyoyev and with Uzbek Foreign Minister Bakhtiyor Saidov
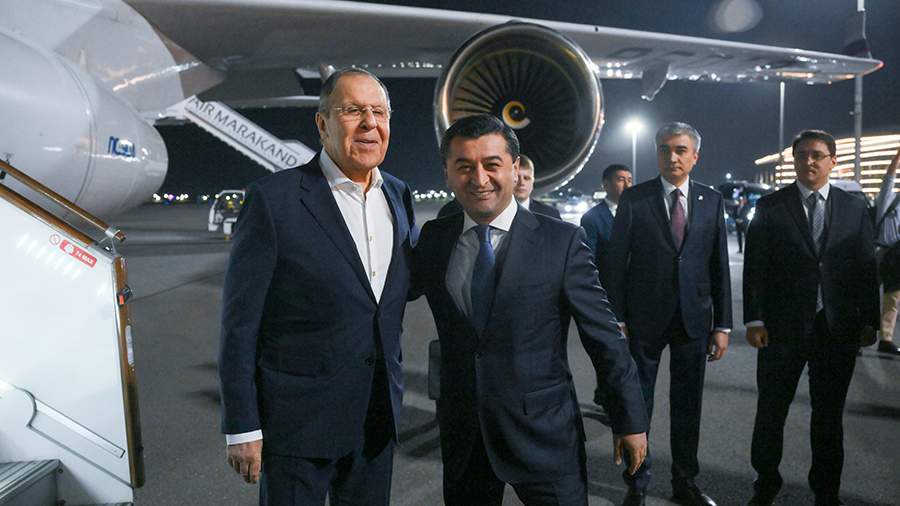

Russian Foreign Minister Sergey Lavrov will meet with Uzbek government officials this week to discuss bilateral relations, Eurasian integration and preparations for the upcoming 80th anniversary of victory over Nazi Germany.
The Russian Foreign Ministry’s official spokeswoman, Maria Zakharova, said Lavrov is expected to meet with Uzbek President Shavkat Mirziyoyev and will hold talks with Uzbek Foreign Minister Bakhtiyor Saidov, TASS reported.
“The sides will discuss current international issues of mutual interest, regional security matters, cooperation within the CIS, SCO and Central Asia-Russia frameworks, taking into account the closeness or similarity between Moscow and Tashkent’s approaches,” Zakharova said adding that “the agenda will also include matters of Eurasian integration processes with Uzbekistan’s observer status in the EAEU in mind.”
During his meetings with leaders of the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) last December, Russian President Vladimir Putin invited them to attend the Victory Day celebrations in Moscow scheduled to be held on May 9.
Also, military units from 19 friendly nations have been invited to participate in the Red Square Parade. The list of these countries has not yet been published, but Uzbek troops marched in the Red Square five years ago, during the 75th anniversary of Victory in the Great Patriotic War.
Uzbekistan traditionally holds numerous Victory Day celebrations and campaigns.
Meanwhile, the Russian Foreign Ministry has emphasized that Moscow and Tashkent have “constructive, respectful and mutually beneficial ties, based on the principles of friendship, sovereign equality and respect to each other’s interests.”
The sides actively cooperate in trade, energy, science and humanitarian affairs.
Special attention will be paid to the issue of labor migrants, as around 1.1 million Uzbek citizens are employed in various sectors in Russia.
Talks will also reportedly include Afghanistan, as this is an important subject for the two nations, TASS reported.
Other regional and global issues are also expected to be touched upon during Lavrov’s meetings with Uzbek officials in Samarkand.
Regional
At least 20 feared killed in militant attack on tourists in Indian Kashmir, security sources say
One security source put the death toll at 20; the second put it at 24 and the third at 26. All three spoke on condition of anonymity as they were not authorised to speak to the media.
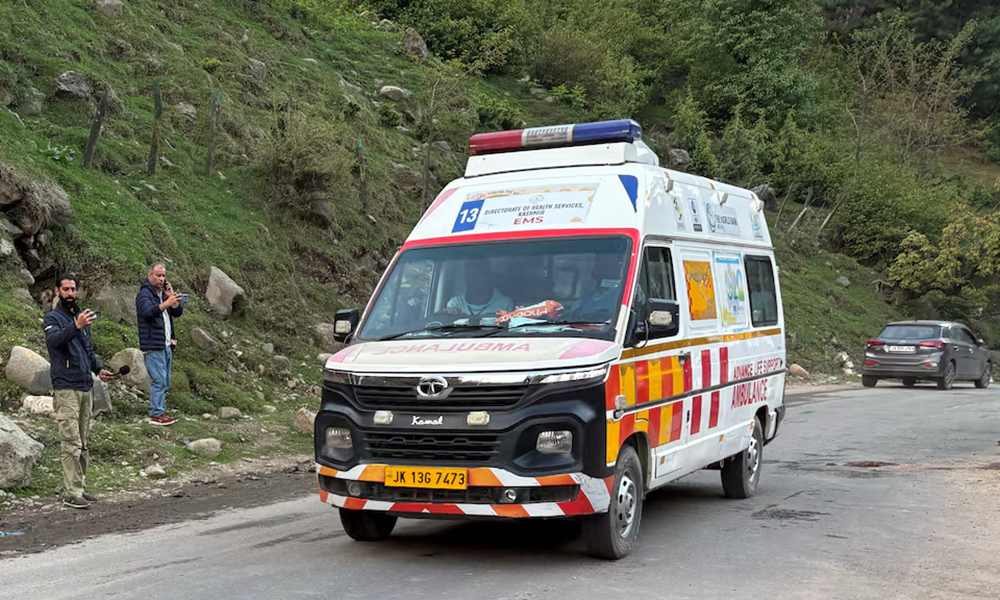

At least 20 people were feared killed after suspected militants opened fire on tourists in India’s Jammu and Kashmir territory on Tuesday, three security sources said, the worst attack on civilians in the troubled Himalayan region for years, Reuters reported.
The attack occurred in Pahalgam, a popular destination in the scenic, mountainous region where mass tourism, especially during the summer, has resurged as Islamist militant violence has eased in recent years.
One security source put the death toll at 20; the second put it at 24 and the third at 26. All three spoke on condition of anonymity as they were not authorised to speak to the media.
“The firing happened in front of us,” one witness told broadcaster India Today, without giving his name. “We thought someone was setting off firecrackers, but when we heard other people (screaming), we quickly got out of there … saved our lives and ran.”
“For four kilometers, we did not stop … I am shaking,” another witness told India Today.
The attack occurred in an off-the-road meadow and two or three militants were involved, the Indian Express newspaper reported, citing an unidentified senior police officer.
“The death toll is still being ascertained so I don’t want to get into those details,” Jammu and Kashmir Chief Minister Omar Abdullah said in a post on X. “Needless to say, this attack is much larger than anything we’ve seen directed at civilians in recent years.”
The nationalities of the victims were not immediately known, read the report.
A little-known militant group, the “Kashmir Resistance,” claimed responsibility for the attack in a social media message. It expressed discontent that more than 85,000 “outsiders” had been settled in the region, spurring a “demographic change”.
“Consequently, violence will be directed toward those attempting to settle illegally,” it said.
Reuters could not independently verify the source of the message.
The regional government of Jammu and Kashmir, where Pahalgam is located, told its legislature this month that nearly 84,000 non-locals, from within India, had been given domicile rights in the territory in the last two years.
“Those behind this heinous act will be brought to justice … They will not be spared!” Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi posted on X. “Their evil agenda will never succeed. Our resolve to fight terrorism is unshakable and it will get even stronger.”
Indian Home Minister Amit Shah said he was rushing to Kashmir to hold a security meeting.
In Washington, the White House said U.S. President Donald Trump had been briefed on what a White House spokesperson described as a “brutal terrorist attack.”
India’s foreign ministry subsequently said Trump called Modi and “expressed full support to India to bring to justice the perpetrators of this heinous attack.”
Militant violence has afflicted the Himalayan region, claimed in full but ruled in part by both India and Pakistan, since an anti-Indian insurgency began in 1989. Tens of thousands of people have been killed, although violence has tapered off in recent years, Reuters reported.
India revoked Kashmir’s special status in 2019, splitting the state into two federally administered territories – Jammu and Kashmir, and Ladakh. The move allowed local authorities to issue domicile rights to outsiders, allowing them to get jobs and buy land in the territory.
That led to a deterioration of ties with Pakistan, which also claims the region. The dispute has spurred bitter animosity and military conflict between the nuclear-armed neighbours.
Attacks targeting tourists in Kashmir have become rare. The last deadly incident took place in June 2024 when at least nine people were killed and 33 injured after a militant attack caused a bus carrying Hindu pilgrims to plunge into a deep gorge.
Some major militant attacks during the height of the insurgency coincided with visits from high-profile foreign officials to India, in likely attempts to draw global attention to Kashmir, Indian security agencies have said.
Tuesday’s attack came a day after U.S. Vice President JD Vance began a four-day, largely personal visit to India.
-

 World4 days ago
World4 days agoThousands of protesters rally against Trump across US
-
 Latest News4 days ago
Latest News4 days agoPolio vaccination campaign launched in Afghanistan
-

 International Sports2 days ago
International Sports2 days agoIPL 2025: Robo-Dog ‘Champak’ explained
-

 International Sports4 days ago
International Sports4 days agoIPL 2025: 14-year-old Vaibhav Suryavanshi becomes youngest IPL player
-

 Latest News3 days ago
Latest News3 days agoAriana Afghan Airlines increases flights to China
-

 Latest News3 days ago
Latest News3 days agoChina invites various Afghan delegations to attend Shanghai forums
-

 World3 days ago
World3 days agoPentagon chief Hegseth shared sensitive Yemen war plans in second Signal chat, source says
-

 Regional3 days ago
Regional3 days agoJD Vance arrives in India, to hold talks with Modi under US tariffs shadow
























