COVID-19
India’s hospitals overrun as COVID-19 infections top global record for 2nd day
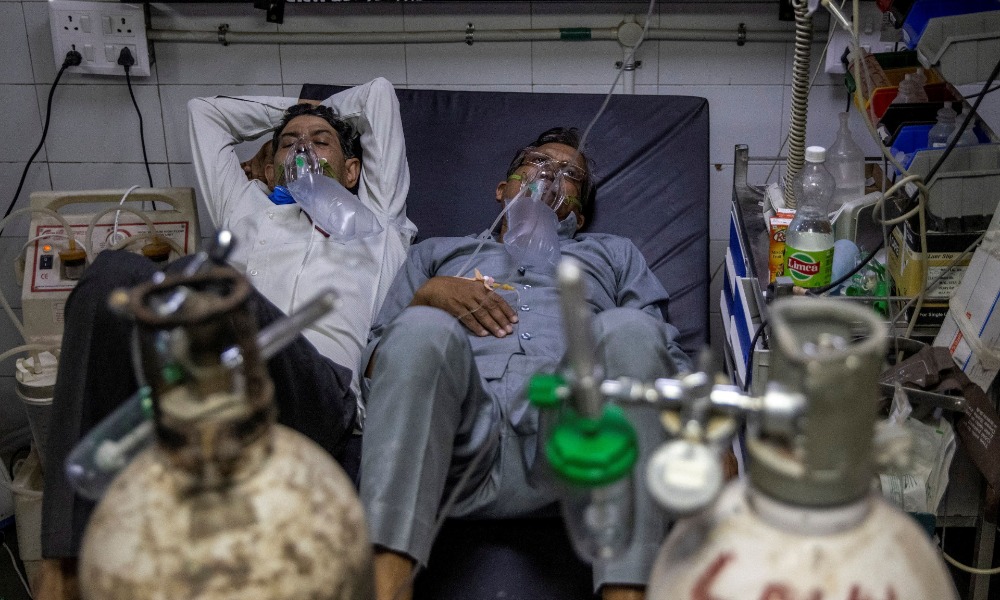
People across India scrambled for life-saving oxygen supplies on Friday and patients lay dying outside hospitals as the capital recorded the equivalent of one death from COVID-19 every five minutes, Reuters reported.
For the second day running, the country’s overnight infection total was higher than ever recorded anywhere in the world since the pandemic began last year, at 332,730.
India’s second wave has hit with such ferocity that hospitals are running out of oxygen, beds and anti-viral drugs. Many patients have been turned away because there was no space for them, doctors in Delhi told Reuters.
Ambulance sirens sounded throughout the day in the deserted streets of the capital, one of India’s worst hit cities, where a lockdown is in place to try and stem the transmission of the virus.
Mass cremations have been taking place as the crematoriums have run out of space.
Reuters reported that at Guru Teg Bahadur Hospital in the north east of the city, critical patients gasping for air arrived in ambulances and autorickshaws. Some waited for hours on trolleys outside and one, Shayam Narayan died before being admitted, a death unlikely to be counted in the city’s rising toll.
“The system is broken,” his younger brother Raj said.
Tushar Maurya, whose mother was being treated inside, urged anyone not in a serious condition to keep away.
“The staff are doing their best but there is not enough oxygen,” she said.
The India Today television channel showed angry relatives outside a hospital in Ahmedabad, the largest city in Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s home state of Gujarat.
“People are dying in front of hospitals while they wait for a bed to become available,” one man said.
Another young man, who was not identified, said: “Is this why we voted for this government? When we need it the most, we find ourselves all alone. Where will the poor go?”
Health experts say India became complacent in the winter, when new cases were running at about 10,000 a day and seemed to be under control, and lifted restrictions to allow big gatherings, Reuters reported.
Modi himself has faced rare criticism for allowing political rallies and a Hindu religious festival, in which millions take a ritual bath in the Ganges river, to go ahead. He addressed many of the rallies with packed crowds and few people wearing masks.
“Indians let down their collective guard,” Zarir Udwadia, a pulmonologist on Maharashtra’s task force, wrote in the Times of India newspaper.
“We heard self-congratulatory declarations of victory from our leaders, now cruelly exposed as mere self-assured hubris.”
Delhi’s government declared in February it had beaten back the coronavirus. On Friday, Chief Minister Arvind Kejriwal went on live television to plead for medical oxygen supplies in a virtual meeting with Modi, warning that many people would die.
“All of the country’s oxygen plants should immediately be taken over by the government through the army,” he said.
Police in the northern state of Uttar Pradesh, some wielding assault rifles, escorted trucks carrying oxygen to waiting hospitals in Delhi, while city governments traded accusations over hoarding.
Modi said the government was making a “continuous effort” to increase oxygen supplies, including steps to divert industrial oxygen.
In Washington, U.S. health officials and a White House spokeswoman on Friday said they were weighing how to help India and had been in contact with officials there, but gave no details on any possible U.S. action.
In Mumbai, a fire broke out in a suburban hospital treating COVID-19 patients early on Friday, killing 13 people. On Wednesday, 22 patients died at a public hospital in Maharashtra where Mumbai is located when oxygen supply ran out due to a leaking tank.
World Health Organization chief Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus said he was concerned about the growing case load in India, which on Thursday passed the previous global high of 297,430 recorded in January in the United States, where case numbers have fallen.
“The situation in India is a devastating reminder of what the virus can do,” he told a virtual briefing in Geneva.
WHO emergencies director Mike Ryan said reducing transmission would be a “very difficult task” but the government was working on limiting mixing between people, which he said was essential, Reuters reported.
Bhramar Mukherjee, a professor of biostatistics and epidemiology at the University of Michigan in the United States, said it seemed as if there was no social safety net for Indians.
“Everyone is fighting for their own survival and trying to protect their loved ones,” he said. “This is hard to watch.”
COVID-19
WHO declares end to COVID global health emergency

The World Health Organization said Friday that COVID-19 no longer qualifies as a global emergency, marking a symbolic end to the devastating coronavirus pandemic that triggered once-unthinkable lockdowns, upended economies and killed millions of people worldwide.
The announcement, made more than three years after WHO declared the coronavirus an international crisis, offers some relief, if not an ending, to a pandemic that stirred fear and suspicion, hand-wringing and finger-pointing across the globe, AP reported.
The U.N. health agency’s officials said that even though the emergency phase was over, the pandemic hasn’t finished, noting recent spikes in cases in Southeast Asia and the Middle East.
WHO says thousands of people are still dying from the virus every week, and millions of others are suffering from debilitating, long-term effects.
“It’s with great hope that I declare COVID-19 over as a global health emergency,” WHO Director-General Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus said.
“That does not mean COVID-19 is over as a global health threat,” he said, warning that new variants could yet emerge. Tedros noted that while the official COVID-19 death toll was 7 million, the real figure was estimated to be at least 20 million.
Tedros said the pandemic had been on a downward trend for more than a year, acknowledging that most countries have already returned to life before COVID-19.
He bemoaned the damage that COVID-19 had done to the global community, saying the pandemic had shattered businesses, exacerbated political divisions, led to the spread of misinformation and plunged millions into poverty.
When the U.N. health agency first declared the coronavirus to be an international crisis on Jan. 30, 2020, it hadn’t yet been named COVID-19 and there were no major outbreaks beyond China.
More than three years later, the virus has caused an estimated 764 million cases globally and about 5 billion people have received at least one dose of vaccine.
In the U.S., the public health emergency declaration made regarding COVID-19 is set to expire on May 11, when wide-ranging measures to support the pandemic response, including vaccine mandates, will end. Many other countries, including Germany, France and Britain, dropped most of their provisions against the pandemic last year.
When Tedros declared COVID-19 to be an emergency in 2020, he said his greatest fear was the virus’ potential to spread in countries with weak health systems.
Most recently, WHO has struggled to investigate the origins of the coronavirus, a challenging scientific endeavor that has also become politically fraught.
COVID-19
COVID-19 in Iran: Nearly 900 new cases, 24 deaths recorded

The Iranian health ministry announced on Sunday that more than 890 new cases of COVID-19 have been identified across the country during the past 24 hours, adding that 24 patients have died in the same period of time, Fars News Agency reported.
“A sum of 891 new patients infected with COVID-19 have been identified in the country based on confirmed diagnosis criteria during the past 24 hours,” the Iranian Health Ministry’s Public Relations Center said on Sunday, adding, “454 patients have been hospitalized during the same time span.”
The ministry’s public relations center said 611 people infected with COVID-19 are in critical condition.
COVID-19
China says 200 million treated, pandemic ‘decisively’ beaten

China says more than 200 million of its citizens have been diagnosed and treated for COVID-19 since it lifted strict containment measures beginning in November.
With 800,000 of the most critically ill patients having recovered, China has “decisively beaten” the pandemic, according to notes from a meeting of the ruling Communist Party’s all-powerful Politburo Standing Committee presided over by President and party leader Xi Jinping, AP reported.
China enforced some of the world’s most draconian lockdowns, quarantines and travel restrictions and still faces questions about the origins of the virus that was first detected in the central Chinese city of Wuhan in late 2019. Heavy-handed enforcement prompted rare anti-government protests and took a heavy toll on the world’s second-largest economy.
The official Xinhua News Agency quoted Xi as saying that policies to control the outbreak had been “entirely correct.” The abrupt lifting in November and December of the “zero COVID” policy that had sought to eliminate all cases of the virus led to a surge in infections that temporarily overwhelmed hospitals.
Case numbers have since peaked and life has largely returned to normal, although international travel in and out of China has yet to return to pre-pandemic levels.
China is now transitioning to a post-pandemic stage after a fight against the outbreak that was “extraordinary in the extreme,” Xinhua said.
The government will continue to “optimize and adjust prevention and control policies and measures according to the times and situations with a strong historical responsibility and strong strategic determination,” Xinhua said.
-

 Latest News4 days ago
Latest News4 days agoMoRRD signs deal for Wakhan road construction
-

 Regional5 days ago
Regional5 days agoPakistan military ends train standoff, says 21 hostages and four troops killed
-

 International Sports5 days ago
International Sports5 days agoBayern’s Harry Kane sets his sights on lifting FIFA Club World Cup trophy
-

 Latest News5 days ago
Latest News5 days agoPakistan Army claims Balochistan train attack orchestrated from Afghanistan
-

 Regional4 days ago
Regional4 days agoSyria keeps role for Islamic law in 5-year transition
-

 Latest News4 days ago
Latest News4 days agoIndia: Pakistan should not blame others for its own failures
-

 Regional4 days ago
Regional4 days agoBlast in northwestern Pakistan mosque injures local Islamist party leader, three others
-

 World4 days ago
World4 days agoTrump says he still has good relations with leader of ‘nuclear power’ North Korea
























