World
Global hunger numbers rose to as many as 828 million in 2021: UN report
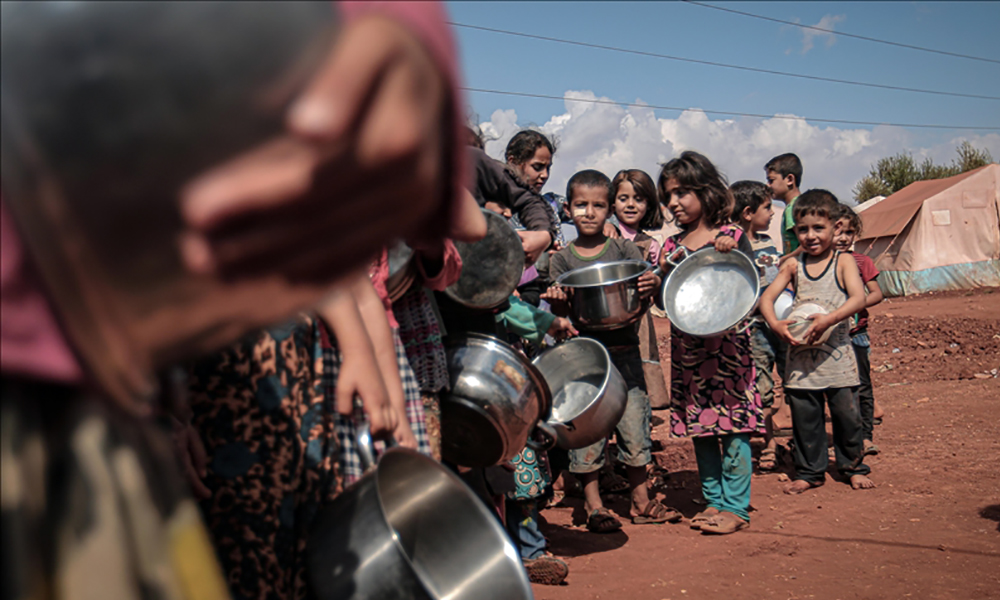

Almost 828 million were affected by hunger globally in 2021, a new United Nations report found, highlighting fresh evidence that the world is moving backwards in its fight to end hunger, food insecurity, and malnutrition.
The new report entitled The State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World (SOFI) found that the number of people suffering from hunger globally increased by almost 46 million since 2020, when the COVID-19 pandemic wreaked havoc on the global economy, and 150 million more since 2019.
The report outlined updates on the global state of food security and nutrition, the latest estimates of the cost and affordability of a healthy diet, and the ways in which governments can repurpose their current support to the agricultural industry and make healthy food cheaper.
Approximately 2.3 billion people (29.3 percent) were moderately or severely food insecure in 2021 – 350 million more compared to before the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic. Almost 924 million people faced food insecurity at severe levels, accounting for an increase of 207 million in just two years.
Speaking at the SOFI launch in New York on Thursday, Deputy Secretary-General Amina Mohammed said that the report’s figures were a “shocking report card of our efforts to end hunger.”
“These are people whose lives, livelihoods and prospects for a fruitful and dignified life are being crippled, with their future eroded and potential aspirations held back,” she added.
Almost 3.1 billion could not afford a healthy diet in 2020, up 112 million from the year before the pandemic, reflecting the economic impacts of the pandemic, such as inflation, and the measures put in place to mitigate the spread of the virus.
Particularly worrying was the fact that an estimated 45 million children under the age of five were suffering from wasting – the deadliest form of malnutrition which involves changes in the way one’s body uses proteins, carbohydrates and fat, leading to involuntary weight loss and muscle mass. Wasting increases the risk of death by up to 12 times, the UN said.
“They need our crosscutting resolve. The evidence presented in this report is compelling as it is outrageous when we see that children in rural settings and poorer households, whose mothers received no formal education, were even more vulnerable to stunting and wasting,” Mohammed said.
The global organization also reported that another 149 million children under the age of five had stunted growth and development due to the lack of essential nutrients in their diet, while 39 million were reported to be overweight.
“These are depressing figures for humanity,” said President of the International Fund for Agricultural Development Gilbert Houngbo.
“We continue to move away from our goal of ending hunger by 2030. The ripple effects of the global food crisis will most likely worsen the outcome again next year. We need a more intense approach to end hunger and IFAD stands ready to do its part by scaling up its operations and impact.”
Ukraine war, climate change are major drivers
Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, which began on February 24 this year, caused immense disruption to the supply of staple cereals, oilseeds, and fertilizer from both nations and global supply chains, the report stated.
This disruption has led to soaring food prices and worsened the state of food insecurity.
Extreme climate events, within the context of this disruption during the Ukraine war, has only made matters worse in low-income countries.
“This report repeatedly highlights the intensification of these major drivers of food insecurity and malnutrition: Conflict, climate extremes, and economic shocks, combined with growing inequalities,” the heads of the five UN agencies involved in the report wrote.
“The issue at stake is not whether adversities will continue to occur or not, but how we must take bolder action to build resilience against future shocks.”
World Food Program chief David Beasley said the “real danger” was that these figures were likely to increase “in the months ahead,” resulting in: “Global destabilization, starvation, and mass migration on an unprecedented scale. We have to act today to avert this looming catastrophe.”
The report urged governments to take immediate action, suggesting they repurpose the resources being used to incentivize production, supply, and consumption of nutritious foods in order to make healthy foods more affordable and to reduce trade barriers to help lower the price of nutritious foods.
World
US readies new Russia sanctions if Putin rejects peace deal, Bloomberg News reports
A State Department spokesperson told Reuters it does not preview sanctions.
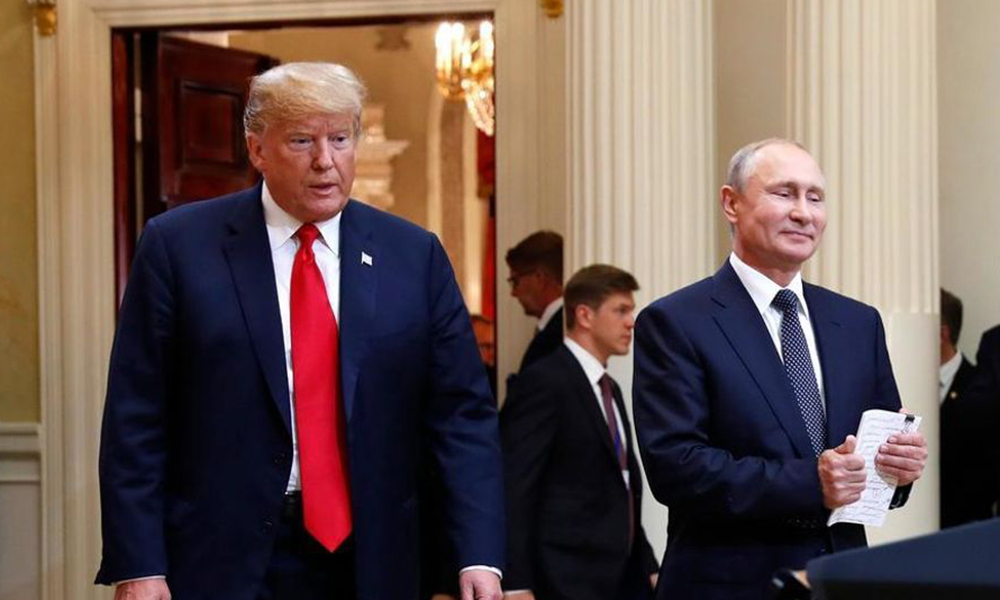

The United States is preparing a further round of sanctions targeting Russia’s energy sector to increase pressure on Moscow should it reject a peace deal with Ukraine, Bloomberg News reported on Wednesday, citing people familiar with the matter.
A White House official told Reuters that U.S. President Donald Trump had made no new decisions regarding Russian sanctions.
“It is the role of agencies to prepare options for the president to execute,” the official said.
Bloomberg had reported the U.S. was considering options including targeting vessels in what is known as Russia’s shadow fleet of tankers used to transport exported oil, as well as traders who facilitate such transactions.
The new measures could be announced as early as this week, the report said, adding that Treasury Secretary Scott Bessent discussed the move with a group of European ambassadors this week.
“It is explicitly false to conclude any decisions have been made regarding future sanctions against Russia. As we have said for months, all options remain on the table in support of President Trump’s tireless efforts to stop the senseless killing, and to achieving a lasting, durable peace,” a U.S. Treasury Department spokesperson said.
A State Department spokesperson told Reuters it does not preview sanctions.
Asked about the Bloomberg article, the Kremlin said it had not seen the report but that any sanctions harm efforts to mend U.S.-Russia relations.
World
Trump adds seven countries, including Syria, to full travel ban list
The White House cited visa overstay rates for Syria in its justification for the ban.

U.S. President Donald Trump on Tuesday expanded a list of countries subject to a full travel ban, prohibiting citizens from an additional seven countries, including Syria, from entering the United States.
The White House said in a statement that Trump signed a proclamation “expanding and strengthening entry restrictions on nationals from countries with demonstrated, persistent, and severe deficiencies in screening, vetting, and information-sharing to protect the Nation from national security and public safety threats.”
Tuesday’s move banned citizens from Burkina Faso, Mali, Niger, South Sudan, Syria and those holding Palestinian Authority-issued travel documents. The action also imposes a full ban on Laos and Sierra Leone, which had previously only been subject to partial restrictions.
The White House said the expanded ban goes into effect on January 1.
The action comes despite Trump’s vow to do everything he could to make Syria successful after landmark talks in November with Syrian President Ahmed al-Sharaa, a former al Qaeda commander who until recently was sanctioned by Washington as a foreign terrorist.
Trump has backed Sharaa, whose visit capped a stunning year for the rebel-turned-ruler who toppled longtime autocratic leader Bashar al-Assad and has since traveled the world trying to depict himself as a moderate leader who wants to unify his war-ravaged nation and end its decades of international isolation.
But in a post on his Truth Social platform on Saturday, Trump vowed “very serious retaliation” after the U.S. military said two U.S. Army soldiers and a civilian interpreter were killed in Syria by a suspected Islamic State attacker who targeted a convoy of American and Syrian forces before being shot dead. He described the incident in remarks to reporters as a “terrible” attack.
The White House cited visa overstay rates for Syria in its justification for the ban.
“Syria is emerging from a protracted period of civil unrest and internal strife. While the country is working to address its security challenges in close coordination with the United States, Syria still lacks an adequate central authority for issuing passports or civil documents and does not have appropriate screening and vetting measures,” the White House said.
Trump signed a proclamation in June banning the citizens of 12 countries from entering the United States and restricting those from seven others, saying it was needed to protect against “foreign terrorists” and other security threats. The bans apply to both immigrants and non-immigrants, such as tourists, students and business travelers.
The travel ban remains on those twelve countries, the White House said.
Trump also added partial restrictions and entry limitations on an additional 15 countries, including Nigeria, which is under scrutiny from Trump, who in early November threatened military action over the treatment of Christians in the country.
Nigeria says claims that Christians face persecution misrepresent a complex security situation and do not take into account efforts to safeguard religious freedom.
Since returning to office in January, Trump has aggressively prioritized immigration enforcement, sending federal agents to major U.S. cities and turning away asylum seekers at the U.S.-Mexico border.
The expansion of the countries subject to entry restrictions marks a further escalation of immigration measures the administration has taken since the shooting of two National Guard members in Washington, D.C., last month.
Investigators say the shooting was carried out by an Afghan national who entered the U.S. in 2021 through a resettlement program under which Trump administration officials have argued there was insufficient vetting.
Days after the shooting, Trump vowed to “permanently pause” migration from all “Third World Countries,” although he did not identify any by name or define the term.
World
Father and son behind Bondi Jewish festival shooting that killed 15, Australian police say
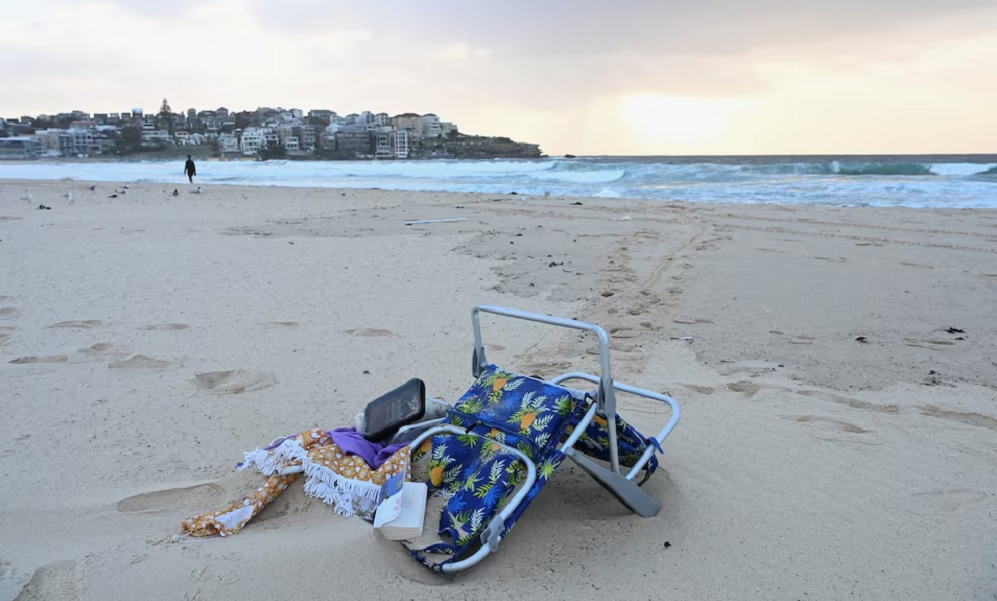

Two alleged gunmen who killed 15 people at a Jewish celebration at Sydney’s Bondi Beach were a father and son, police said on Monday, as Australia began mourning victims of its worst gun violence in almost 30 years.
The father, a 50-year-old, was killed at the scene, taking the number of dead to 16, while his 24-year-old son was in a critical condition in hospital, police said at a press conference on Monday. The father and son were identified as Sajid Akram and Naveed Akram, respectively, by state broadcaster ABC and other local media outlets, Reuters reported.
Officials have described Sunday’s shooting as a targeted antisemitic attack.
Forty people remain in hospital following the attack, including two police officers who are in a serious but stable condition, police said. The victims were aged between 10 and 87.
Witnesses said the attack at the famed beach, which was packed on a hot evening, lasted about 10 minutes, sending hundreds of people scattering along the sand and into nearby streets.
Police said around 1,000 people had attended the targeted Hanukkah event, which was held in a small park off the beach.
A bystander captured on video tackling and disarming an armed man during the attack has been hailed as a hero whose actions saved lives. 7News Australia named him as Ahmed al Ahmed, citing a relative, who said the 43-year-old fruit shop owner had been shot twice and had undergone surgery.
A fundraising page for the man had raised more than A$350,000 ($233,000) by Monday afternoon.
Police did not release the shooters’ names, but said the father had held a firearms license since 2015 and had six licensed weapons.
Home Minister Tony Burke said the father arrived in Australia in 1998 on a student visa, while his son is an Australian-born citizen.
Police did not provide details about the firearms, but videos from the scene showed the men firing what appeared to be a bolt-action rifle and a shotgun.
“We are very much working through the background of both persons. At this stage, we know very little about them,” New South Wales Police Commissioner Mal Lanyon told reporters.
Bondi local Morgan Gabriel, 27, said she had been heading to a nearby cinema when she heard what she thought were fireworks, before people started running up her street.
“I sheltered about six or seven. Two of them were actually my close friends, and the rest were just people that were on the street. But people, their phones had been left down the beach, and everyone was just trying to get away,” she said.
“It’s a very sad time this morning… Normally, like on a Monday or any morning, it’s packed. People are swimming, surfing, running. So this is very, very quiet. And there’s definitely a solemn sort of vibe.”
A makeshift memorial with flowers and Israeli and Australian flags was set up at the Bondi pavilion and an online condolence book was established. Police and private Jewish security guards wearing earpieces were positioned around as mourners paid respects and laid flowers.
WORLD LEADERS CONDEMN THE ATTACK
Authorities said they were confident only two attackers were involved in the incident, after previously saying they were checking whether a third offender was involved.
At the suspects’ home in Bonnyrigg, a suburb around 36 km (22 miles) west of the CBD, there was a heavy police presence on Monday, with a cordon wrapping around several neighbouring houses.
Australian Prime Minister Anthony Albanese visited Bondi Beach on Monday morning to lay flowers near the scene of the attack.
“What we saw yesterday was an act of pure evil, an act of antisemitism, an act of terrorism on our shores in an iconic Australian location,” Albanese told reporters.
“The Jewish community are hurting today. Today, all Australians wrap our arms around them and say, we stand with you. We will do whatever is necessary to stamp out antisemitism. It is a scourge, and we will eradicate it together.”
Albanese later urged Australians to light a candle in solidarity with the Jewish community “to show that light will indeed defeat darkness – part of what Hanukkah celebrates”, he said.
Albanese said several world leaders including U.S. President Donald Trump and French President Emmanuel Macron had reached out and offered condolences and support.
Sunday’s shootings were the most serious in a string of antisemitic attacks on synagogues, buildings and cars in Australia since the beginning of Israel’s war in Gaza in October 2023.
Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu said he had warned Albanese that Australia’s support for Palestinian statehood would fuel antisemitism.
In August, Australia accused Iran of directing at least two antisemitic attacks and gave Tehran’s ambassador a week to leave the country.
‘SAW BODIES ON THE GROUND’
Mass shootings are rare in Australia, one of the world’s safest countries. Sunday’s attack was the worst since 1996, when a gunman killed 35 people at the Port Arthur tourist site in the southern island state of Tasmania.
Rabbi Mendel Kastel, whose brother-in-law Eli Schlanger was killed in Sunday’s attack, said it had been a harrowing evening.
“You can very easily become very angry and try to blame people, turn on people but that’s not what this is about. It’s about a community,” he said.
“We need to step up at a time like this, be there for each other, and come together. And we will, and we will get through this, and we know that. The Australian community will help us do it,” he added.
Local woman Danielle, who declined to give her surname, was at the beach when the shooting occurred and raced to collect her daughter, who was attending a bar mitzvah at a function centre near where the alleged shooters were positioned.
“I heard there was a shooting so I bolted there to get my daughter, I could hear gunshots, I saw bodies on the ground. We are used to being scared, we have felt this way since October 7.”
Hamas militants attacked Israel on October 7, 2023, killing around 1,200 people, according to Israeli tallies. The attack precipitated Israel’s war in Gaza, which has killed more than 70,000 Palestinians, according to Gaza health authorities.
Australia’s Jewish diaspora is small but deeply embedded in the wider community, with about 150,000 people who identify as Jewish in the country of 27 million. About one-third of them are estimated to live in Sydney’s eastern suburbs, including Bondi.
Major cities including Berlin, London and New York stepped up security around Hanukkah events on Sunday following the attack at Bondi.
-

 Latest News4 days ago
Latest News4 days agoUS delivers second batch of Afghan Black Hawk helicopters to Peru
-

 Latest News3 days ago
Latest News3 days agoGermany speeds up admission of Afghans from Pakistan
-

 Sport3 days ago
Sport3 days agoIPL 2026 Auction set for Abu Dhabi with $28.6 million purse at stake
-

 Business4 days ago
Business4 days agoAfghan economy posts second year of growth despite deep structural challenges
-

 Latest News3 days ago
Latest News3 days agoAfghanistan to establish independent oil and gas authority
-

 Sport4 days ago
Sport4 days agoATN to broadcast ‘The Best FIFA Football Awards 2025’
-

 Latest News3 days ago
Latest News3 days agoUS intelligence chief warns of ‘direct threat’ from suspected terrorists inside the country
-

 International Sports4 days ago
International Sports4 days agoILT20: Jahangir powers Dubai Capitals to nine-run win over Abu Dhabi Knight Riders