Science & Technology
Foxconn iPhone India output drops 50% amid COVID surge
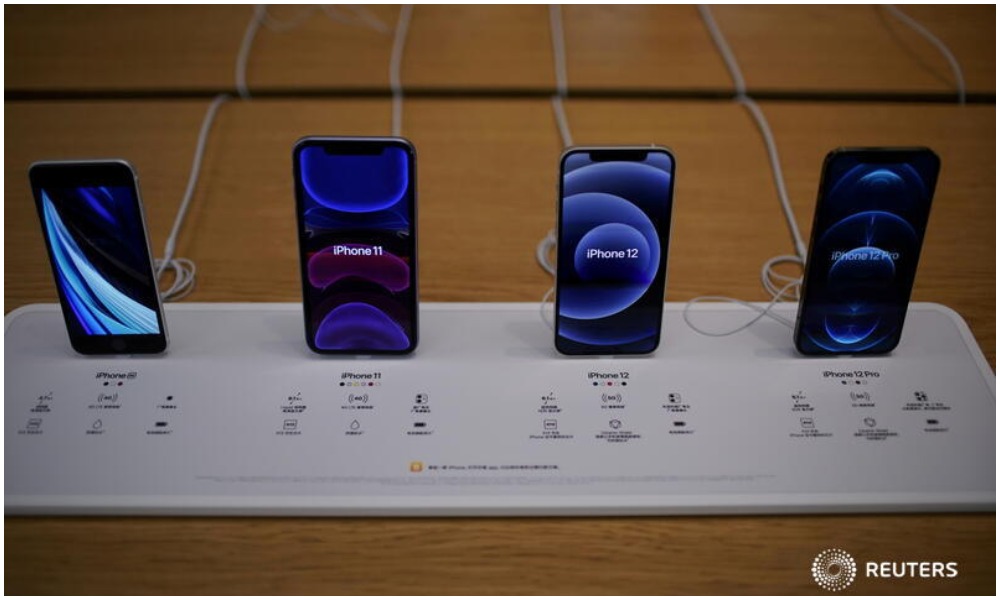

Production of the Apple iPhone 12 at a Foxconn factory in India has slumped by more than 50% because workers infected with COVID-19 have had to leave their posts, two sources told Reuters.
The Foxconn facility in the southern state of Tamil Nadu produces iPhones specifically for India, the world’s No.2 smartphone market.
Tamil Nadu is one of the worst hit states in the second coronavirus wave engulfing India. Officials imposed a full lockdown in the state from Monday, closing public transport and shuttering shops, to try slow surging infectionsm Reuters reported.
More than 100 Foxconn employees in the state have tested positive for COVID-19 and the company has enforced a no-entry ban at its factory in the capital of Chennai until late May, one of the sources said.
“Employees are only allowed to leave but not to enter the facility since yesterday,” the person said. “Only a small part of output is being kept.”
More than 50% of the plant’s capacity had been cut, both sources said, declining to be named as they were not authorised to speak to the media.
They did not specify the plant’s capacity and it was unclear how many workers were at the facility, which provides dormitory accommodation for employees.
Taipei-based Foxconn, the world’s largest contract electronics maker and a major supplier to Apple, said a small number of employees at one of its facilities in India tested positive for COVID-19 and the company was providing them with support, including medical assistance, Reuters reported.
“Foxconn places the health and safety of our employees as our highest priority and that is why we have been working closely with local government and public health authorities in India to address the challenges that we and all companies are facing in dealing with the COVID-19 crisis,” it said in a statement to Reuters.
Foxconn declined to comment on factory output or specific staffing levels. Apple did not immediately respond to a request for comment.
India has benefited from Apple’s move to shift some areas of production from China to other markets as it navigates a trade war between Washington and Beijing, with Apple announcing in March it had started the assembly of the iPhone 12 in India.
International Sports
IPL 2025: Robo-Dog ‘Champak’ explained
Covered in a brown fur-like print and fitted with a camera in place of a face, the robot is designed to offer dynamic, on-ground visuals from a dog’s eye view
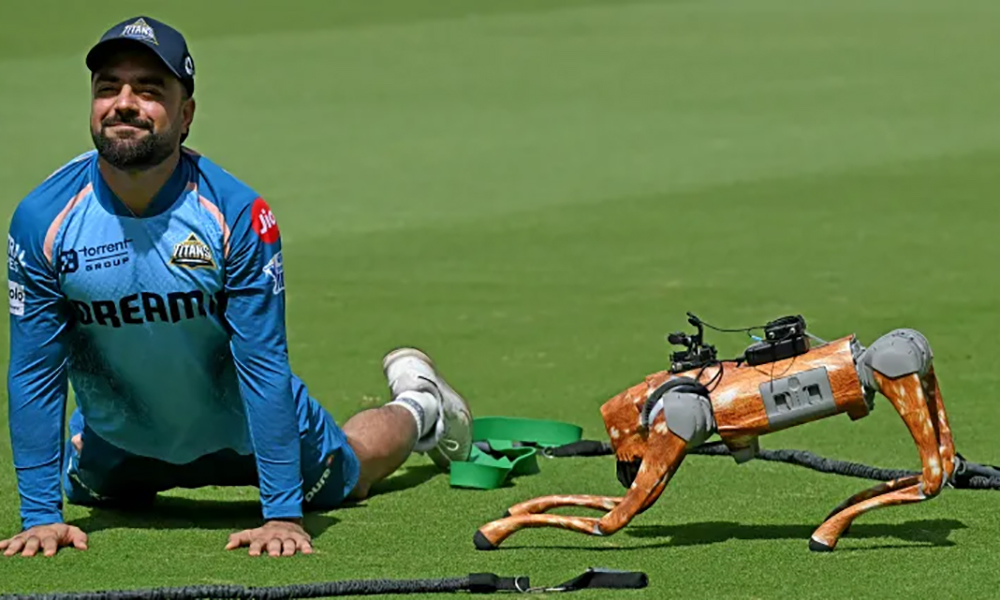

Organizers of this year’s Indian Premier League (IPL) are blazing a trail when it comes to embracing cutting edge technology and over the past week have deployed an AI-powered robotic dog that is fast growing in popularity among both players and fans.
The mechanical camera-carrying canine, named Champak, is the latest addition to the league’s broadcast team and was introduced to the public before the Delhi Capitals and Mumbai Indians match at the Arun Jaitley Stadium on April 13.
Former New Zealand cricketer and commentator Danny Morrison formally introduced his new broadcast companion before demonstrating the IPL robot dog’s ability to run, jump, respond to various voice commands and even draw a heart shape with its front limbs.
The video clip, put out by the IPL’s social media handles, also shows Mumbai Indians’ players Hardik Pandya, Reece Topley and Delhi Capitals captain Axar Patel interacting with the robot dog and having a blast.
The IPL also called on fans to help name the robot dog, which has been a regular part of the broadcast team in subsequent matches. Fan votes eventually saw the robotic canine named Champak.
During the Lucknow Super Giants vs Chennai Super Kings clash in Lucknow, MS Dhoni couldn’t resist a little fun with the robo-dog – playfully lifting it up and putting it down sideways, much to the crowd’s delight.
Known for his love of dogs, often seen in heart-warming moments with his own pets on social media, MS Dhoni later scooped up the mechanical pup and carried it off, probably for some extra playtime.
Covered in a brown fur-like print and fitted with a camera in place of a face, the robot is designed to offer dynamic, on-ground visuals from a dog’s eye view, bringing fans closer to the action in new and immersive ways.
Comparable to a GoPro-like action cameras, the robot dog enables unique broadcast angles along the sidelines and pitch perimeter.
The IPL robot dog draws clear inspiration from the quadrupeds designed by United States-based robotics company Boston Dynamics.
Similar quadrupeds have been deployed from military logistics to hazardous site inspections. The IPL’s version appears to be a small and playful adaptation.
Have you seen Champak yet?
For cricket fans across the country, tune in today, Monday April 22, to watch Lucknow Super Giants take on Delhi Capitals. The match starts at 5pm Kabul time.
Ariana Television will broadcast the match live and exclusively across Afghanistan and hopefully Champak will once again be out of the field for fans to see.
Science & Technology
NASA rover finds fresh evidence of the warm and wet past of Mars
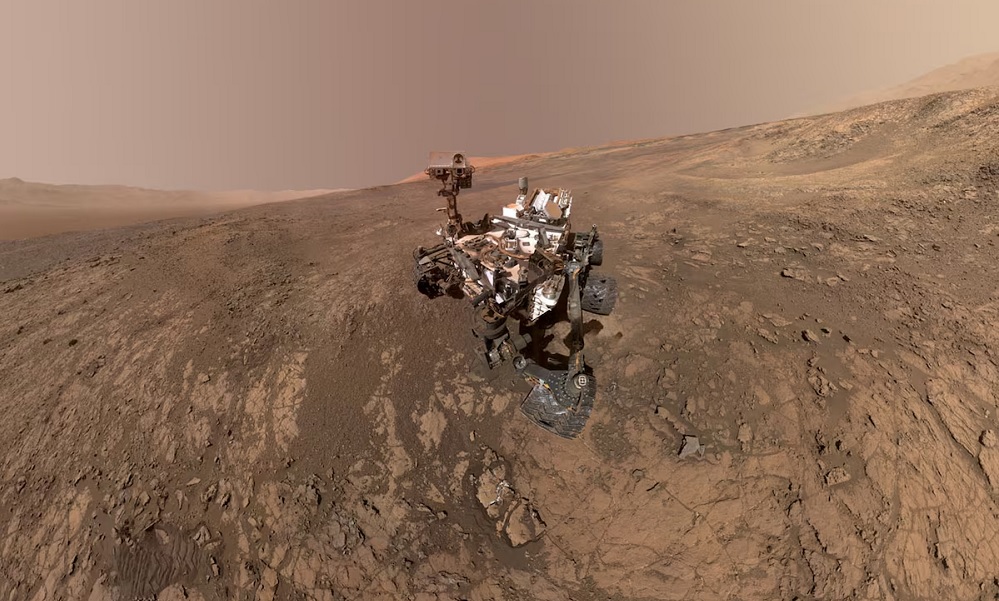

A mineral called siderite found abundantly in rock drilled by a NASA rover on the surface of Mars is providing fresh evidence of the planet’s warmer and wetter ancient past when it boasted substantial bodies of water and potentially harbored life.
The Curiosity rover, which landed on Mars in 2012 to explore whether Earth’s planetary neighbor was ever able to support microbial life, found the mineral in rock samples drilled at three locations in 2022 and 2023 inside Gale crater, a large impact basin with a mountain in the middle, Reuters reported.
Siderite is an iron carbonate mineral. Its presence in sedimentary rocks formed billions of years ago offers evidence that Mars once had a dense atmosphere rich in carbon dioxide, a gas that would have warmed the planet through the greenhouse effect to the point that it could sustain bodies of liquid water on its surface.
There are features on the Martian landscape that many scientists have interpreted as signs that liquid water once flowed across its surface, with potential oceans, lakes and rivers considered as possible habitats for past microbial life.
Carbon dioxide is the main climate-regulating greenhouse gas on Earth, as it is on Mars and Venus. Its presence in the atmosphere traps heat from the sun, warming the climate.
Until now, evidence indicating the Martian atmosphere previously was rich in carbon dioxide has been sparse. The hypothesis is that when the atmosphere – for reasons not fully understood – evolved from thick and rich in carbon dioxide to thin and starved of this gas, the carbon through geochemical processes became entombed in rocks in the planet’s crust as a carbonate mineral.
The samples obtained by Curiosity, which drills 1.2 to 1.6 inches (3-4 centimeters) down into rock to study its chemical and mineral composition, lend weight to this notion. The samples contained up to 10.5% siderite by weight, as determined by an instrument onboard the car-sized, six-wheeled rover.
“One of the longstanding mysteries in the study of Martian planetary evolution and habitability is: if large amounts of carbon dioxide were required to warm the planet and stabilize liquid water, why are there so few detections of carbonate minerals on the Martian surface?” said University of Calgary geochemist Benjamin Tutolo, a participating scientist on NASA’s Mars Science Laboratory Curiosity rover team and lead author of the study published on Thursday in the journal Science, opens new tab.
“Models predict that carbonate minerals should be widespread. But, to date, rover-based investigations and satellite-based orbital surveys of the Martian surface had found little evidence of their presence,” Tutolo added.
Because rock similar to that sampled by the rover has been identified globally on Mars, the researchers suspect it too contains an abundance of carbonate minerals and may hold a substantial portion of the carbon dioxide that once warmed Mars.
The Gale crater sedimentary rocks – sandstones and mudstones – are thought to have been deposited around 3.5 billion years ago, when this was the site of a lake and before the Martian climate underwent a dramatic change.
“The shift of Mars’ surface from more habitable in the past, to apparently sterile today, is the largest-known environmental catastrophe,” said planetary scientist and study co-author Edwin Kite of the University of Chicago and Astera Institute.
“We do not know the cause of this change, but Mars has a very thin carbon dioxide atmosphere today, and there is evidence that the atmosphere was thicker in the past. This puts a premium on understanding where the carbon went, so discovering a major unsuspected deposit of carbon-rich materials is an important new clue,” Kite added.
The rover’s findings offer insight into the carbon cycle on ancient Mars.
On Earth, volcanoes spew carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, and the gas is absorbed by surface waters – mainly the ocean – and combines with elements such as calcium to form limestone rock. Through the geological process called plate tectonics, this rock is reheated and the carbon is ultimately released again into the atmosphere through volcanism. Mars, however, lacks plate tectonics.
“The important feature of the ancient Martian carbon cycle that we outline in this study is that it was imbalanced. In other words, substantially more carbon dioxide seems to have been sequestered into the rocks than was subsequently released back into the atmosphere,” Tutolo said.
“Models of Martian climate evolution can now incorporate our new analyses, and in turn, help to refine the role of this imbalanced carbon cycle in maintaining, and ultimately losing, habitability over Mars’ planetary history,” Tutolo added.
Science & Technology
Meta releases new AI model Llama 4
Meta said in a statement that the Llama 4 Scout and Llama 4 Maverick are its “most advanced models yet” and “the best in their class for multimodality.”

Meta Platforms on Saturday released the latest version of its large language model (LLM) Llama, called the Llama 4 Scout and Llama 4 Maverick.
Meta said Llama is a multimodal AI system. Multimodal systems are capable of processing and integrating various types of data including text, video, images and audio, and can convert content across these formats.
Meta said in a statement that the Llama 4 Scout and Llama 4 Maverick are its “most advanced models yet” and “the best in their class for multimodality.”
Meta added that Llama 4 Maverick and Llama 4 Scout will be open source software. It also said it was previewing Llama 4 Behemoth, which it called “one of the smartest LLMs in the world and our most powerful yet to serve as a teacher for our new models.”
Big technology firms have been investing aggressively in artificial intelligence (AI) infrastructure following the success of OpenAI’s ChatGPT, which altered the tech landscape and drove investment into machine learning.
The Information reported on Friday that Meta had delayed the launch of its LLM’s latest version because during development, Llama 4 did not meet Meta’s expectations on technical benchmarks, particularly in reasoning and math tasks.
The company was also concerned that Llama 4 was less capable than OpenAI’s models in conducting humanlike voice conversations, the report added.
Meta plans to spend as much as $65 billion this year to expand its AI infrastructure, amid investor pressure on big tech firms to show returns on their investments.
-

 Latest News5 days ago
Latest News5 days agoEngagement and diplomacy key to solving Afghanistan’s challenges, says Ratwatte
-

 Sport4 days ago
Sport4 days agoAfghanistan qualify for U19 Cricket World Cup 2026
-

 Regional4 days ago
Regional4 days agoDeadliest US strike in Yemen kills 74 at oil terminal, Houthis say
-

 World3 days ago
World3 days agoThousands of protesters rally against Trump across US
-

 World4 days ago
World4 days agoIran, US end nuclear talks in Rome, agree to meet next week
-
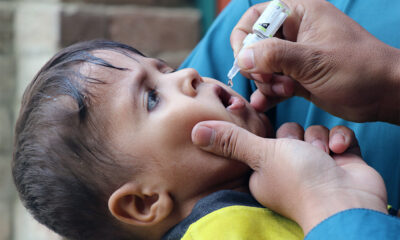
 Latest News3 days ago
Latest News3 days agoPolio vaccination campaign launched in Afghanistan
-

 International Sports3 days ago
International Sports3 days agoIPL 2025: 14-year-old Vaibhav Suryavanshi becomes youngest IPL player
-

 Latest News2 days ago
Latest News2 days agoChina invites various Afghan delegations to attend Shanghai forums
























