Health
A new global health emergency: Mpox
The announcement by WHO director-general Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus came after a meeting of the U.N. health agency’s emergency committee
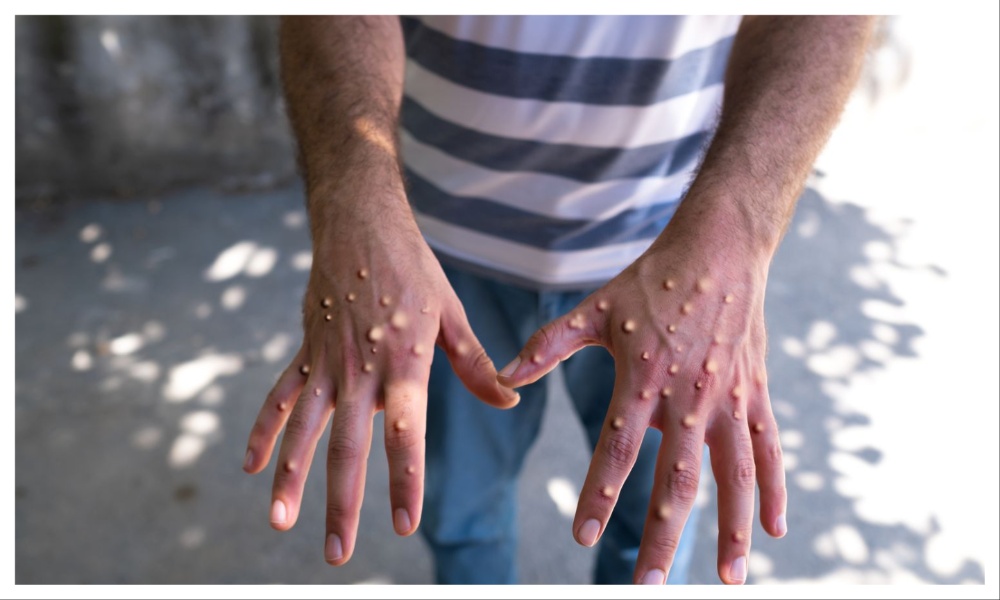

The World Health Organization declared Wednesday that the increasing spread of mpox in Africa is a global health emergency, warning the virus might ultimately spill across international borders.
The announcement by WHO director-general Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus came after a meeting of the U.N. health agency’s emergency committee.
The Africa Centers for Disease Control and Prevention declared mpox a public health emergency on the continent on Tuesday.
WHO said there have been more than 14,000 cases and 524 deaths in Africa this year, which already exceed last year’s figures.
So far, more than 96 percent of all cases and deaths are in a single country — Congo. Scientists are concerned by the spread of a new version of the disease there that might be more easily transmitted among people, Associated Press reported.
Here’s a look at what we know about mpox, and what might be done to contain it:
What is mpox?
Mpox, also known as monkeypox, was first identified by scientists in 1958 when there were outbreaks of a “pox-like” disease in monkeys.
Until recently, most human cases were seen in people in central and West Africa who had close contact with infected animals.
Mpox belongs to the same family of viruses as smallpox but causes milder symptoms like fever, chills and body aches. People with more serious cases can develop lesions on the face, hands, chest and genitals.
What’s happening in Africa that’s causing all this concern?
The number of cases has jumped dramatically. Last week, the Africa CDC reported that mpox has now been detected in at least 13 African countries. Compared with the same period last year, the agency said cases are up 160 percent and deaths have increased by 19 percent.
Earlier this year, scientists reported the emergence of a new form of mpox in a Congolese mining town that can kill up to 10 percent of people and may spread more easily.
WHO said mpox was recently identified for the first time in four East African countries: Burundi, Kenya, Rwanda and Uganda. All of those outbreaks were linked to the epidemic in Congo. Tedros said there was concern for the further spread of the disease within Africa and beyond.
In the Ivory Coast and South Africa, health authorities have reported outbreaks of a different and less dangerous version of mpox that spread worldwide in 2022.
What does an emergency declaration mean?
WHO’s emergency declaration is meant to spur donor agencies and countries into action. But the global response to previous declarations has been mixed.
Africa CDC Director General Dr. Jean Kaseya said the agency’s declaration of a public health emergency was meant “to mobilize our institutions, our collective will and our resources to act swiftly and decisively.” He appealed to Africa’s international partners for help, saying that the escalating caseload in Africa had largely been ignored.
Greg Ramm, Save the Children’s Congo director, said the organization was particularly worried about the spread of mpox in the crowded camps for refugees in the east, noting there were 345,000 children “crammed into tents in unsanitary conditions.”
He said the country’s health system was already “collapsing” under the strain of malnutrition, measles and cholera.
WHO had already released $1.45 million from its emergency fund to support the response to mpox in Africa, but said it needs an initial $15 million to fund that response.
Health
Japanese charity Peshawar-Kai to resume leprosy treatment in Afghanistan
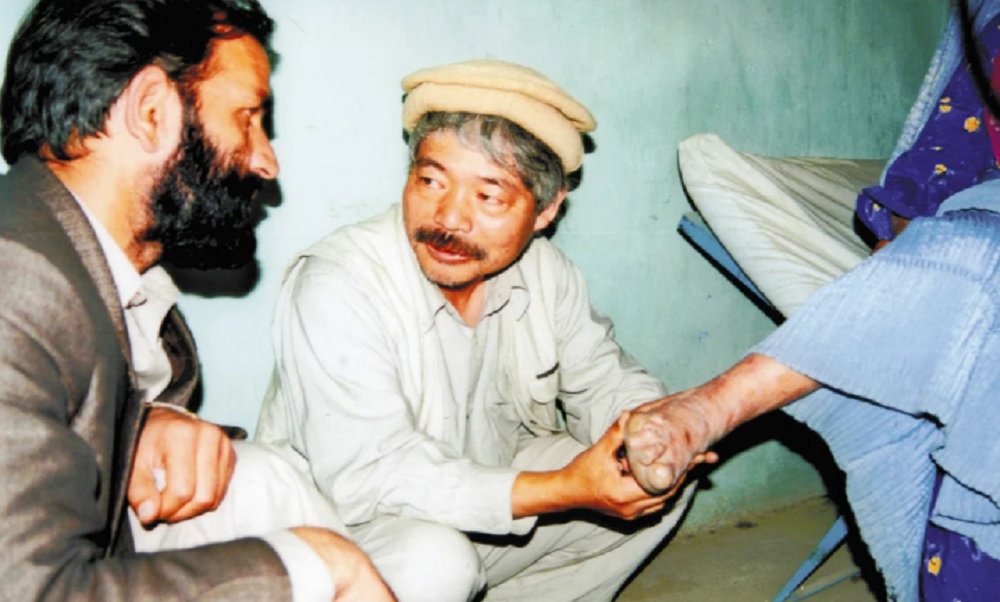
Peshawar-Kai, a Japanese aid organization, has announced that it will resume leprosy treatment in Afghanistan after around 15 years.
The charity will treat leprosy patients in memory of its former head Tetsu Nakamura, Japan’s Yomiuri Shimbun newspaper reported.
The NGO will begin its leprosy treatment program in Afghanistan this year.
It will treat patients in areas such as Nangarhar province by providing medicines, training staff and sending mobile treatment teams.
Leprosy, also known as Hansen disease, is a chronic infectious disease caused mainly by a type of bacteria called Mycobacterium leprae. The disease affects the skin, the peripheral nerves, the mucosa of the upper respiratory tract and the eyes.
Nakamura started treated leprosy patients in Pakistan in the 1980s and then began extensive activities, including the construction of water supply canals in Afghanistan.
The Japanese aid worker was killed in an armed attack in Jalalabad in December 2019.
Health
WHO confirms second Polio case in Afghanistan
The Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan’s Public Health Ministry has not yet commented.
The World Health Organization (WHO) has confirmed the second case of polio in Afghanistan for the year 2025.
The case was identified in March in Helmand province.
This follows the first reported case in the Bala Murghab district of Badghis province, where a five-year-old girl was diagnosed with the virus.
Additionally, 18 environmental samples testing positive for the polio virus have been reported in provinces including Kandahar, Helmand, Kabul, Laghman, Nangarhar, and Zabul.
Afghanistan and Pakistan remain the only countries where polio has not been eradicated.
Polio is a viral disease for which there is no cure, and vaccination is the only way to protect children from it.
The Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan’s Public Health Ministry has not yet commented.
Health
Afghanistan strengthens healthcare system through collaborations with UNDP and UNFPA
Among those who Jalali met with were Stephen Rodriques, UNDP representative to Afghanistan, and Koffi Kwabena Asante, the UNFPA representative to Afghanistan.

In a series of high-level meetings Mawlawi Noor Jalal Jalali, Minister of Public Health of the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan (IEA), has engaged with key international partners in a bid to bolster Afghanistan’s healthcare infrastructure.
Among those who Jalali met with were Stephen Rodriques, United Nations Development Programme’s (UNDP) representative to Afghanistan, and Koffi Kwabena Asante, the United Nations Population Fund (UNFPA) representative to Afghanistan.
Discussions between them highlighted the importance of collaborative efforts to address the country’s most pressing health challenges and ensure long-term, sustainable improvements.
The first meeting with Rodriques focused on the deployment of solar energy solutions to power healthcare centers across Afghanistan, particularly in remote and underserved areas.
Both parties explored the criteria for selecting appropriate sites for these solar-powered initiatives, underscoring the critical role of renewable energy in enhancing healthcare access.
The dialogue also covered integrated approaches to combat endemic diseases such as malaria, tuberculosis, and HIV/AIDS.
Jalali emphasized the importance of effective disease control, which, he noted, requires precise coordination and operational transparency to ensure impactful service delivery.
In response, Rodriques reaffirmed UNDP’s commitment to maintaining transparency and accountability in its interventions, pledging continued support for strengthening Afghanistan’s healthcare system.
The second round of discussions with UNFPA representatives Koffi Kwabena Asante and Andrew Saberton revolved around revitalizing the Afghan health sector, securing sustained financial support, and optimizing aid management.
Jalali stressed the need for a strategic overhaul of resource allocation to optimize international assistance and align efforts with national health priorities.
The discussions also delved into transitioning mobile health teams into permanent centers to expand healthcare access, as well as enhancing service delivery in line with the ministry’s health policy.
Jalali reiterated the importance of transparency in resource management to ensure the efficacy and sustainability of healthcare services.
Saberton commended the Afghan government’s commitment to these principles and assured that UNFPA would continue to provide vital resources to improve health outcomes in Afghanistan.
Both meetings highlighted the shared vision of fostering greater transparency, accountability, and long-term sustainability in Afghanistan’s healthcare system.
Through strategic collaborations with UNDP and UNFPA, Jalali aims to drive impactful reforms that will improve healthcare access and outcomes across the country.
The commitment of both organizations to supporting Afghanistan’s healthcare sector underscores the importance of international partnerships in tackling complex health challenges and ensuring the well-being of the Afghan people.
-

 Latest News5 days ago
Latest News5 days agoOver 250,000 Afghan refugees return home from Pakistan and Iran in April
-

 Business5 days ago
Business5 days agoChinese company keen to invest $50 million in automobile industry in Afghanistan
-

 International Sports5 days ago
International Sports5 days agoHarry Kane claims first career title as Bayern Munich win 34th Bundesliga title
-

 Sport5 days ago
Sport5 days agoAfghanistan climb to No.7 in ICC ODI rankings
-

 Regional4 days ago
Regional4 days agoIran’s foreign minister urges restraint in India, Pakistan standoff
-

 Latest News4 days ago
Latest News4 days agoCabinet Meeting convened to discuss Afghanistan’s population census plan
-

 International Sports4 days ago
International Sports4 days agoIPL 2025: Seven teams fighting for four spots
-

 World4 days ago
World4 days agoIsrael may seize all Gaza in expanded operation, officials say
























