COVID-19
Afghanistan marks one year of Coronavirus
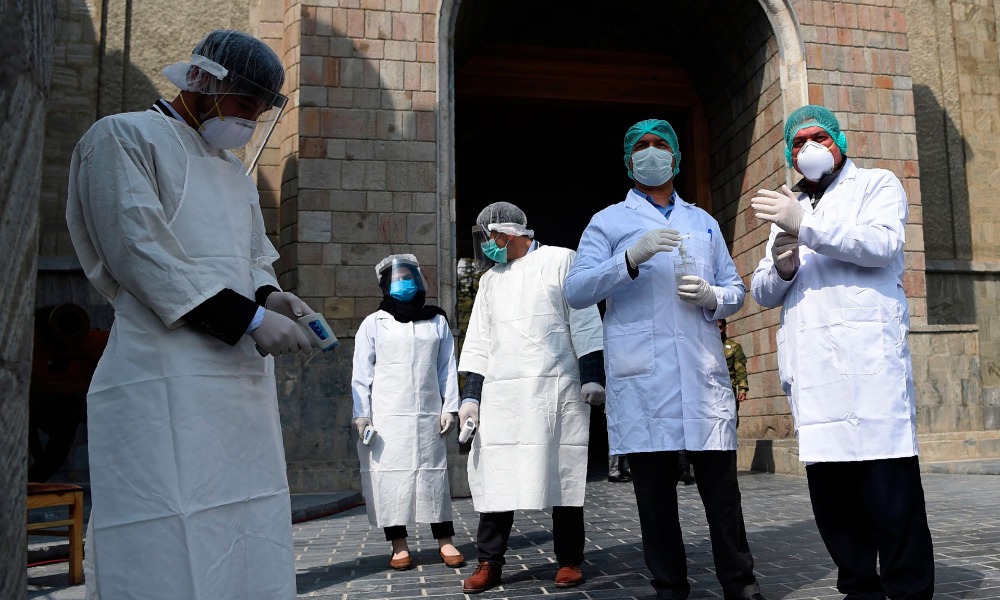

One year ago today, February 24, the first case of COVID-19 was recorded in Herat, after which the virus gradually spread to all provinces of Afghanistan.
Over the course of the year, nearly 2,500 people have died from the disease in Afghanistan, and over 55,000 positive cases have been recorded.
Coinciding with the one-year infection anniversary, Afghanistan’s vaccine program was officially launched in Herat, with health workers receiving the first shots.
In the past year, 9,222 people were infected with the virus in Herat, of which 431 died. Of these, 296 are men and 135 are women. Officials at the Herat Public Health Department said to date seven doctors in Herat alone have died from the virus.
Herat meanwhile was not only the first hotspot in the country - but it has also suffered a serious second wave, which led to a total lockdown of the city.
As a result, government has, in just three weeks, completed a 100-bed hospital for COVID-19 patients.
New cases have meanwhile started to subside.
On Tuesday, the first vaccines - the Covishield vaccine supplied by India - were administered in Kabul at a ceremony attended by President Ashraf Ghani. The first recipients were health workers, security force members and journalists.
India donated 500,000 doses of AstraZeneca COVID-19 vaccine earlier this month.
The Public Health Ministry said that 250,000 people – mostly health workers and Afghan security forces and media workers – would be inoculated in the first stage.
The vaccine is now being administered in three provinces - Kabul, Herat and Baghlan.
COVID-19
WHO declares end to COVID global health emergency

The World Health Organization said Friday that COVID-19 no longer qualifies as a global emergency, marking a symbolic end to the devastating coronavirus pandemic that triggered once-unthinkable lockdowns, upended economies and killed millions of people worldwide.
The announcement, made more than three years after WHO declared the coronavirus an international crisis, offers some relief, if not an ending, to a pandemic that stirred fear and suspicion, hand-wringing and finger-pointing across the globe, AP reported.
The U.N. health agency’s officials said that even though the emergency phase was over, the pandemic hasn’t finished, noting recent spikes in cases in Southeast Asia and the Middle East.
WHO says thousands of people are still dying from the virus every week, and millions of others are suffering from debilitating, long-term effects.
“It’s with great hope that I declare COVID-19 over as a global health emergency,” WHO Director-General Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus said.
“That does not mean COVID-19 is over as a global health threat,” he said, warning that new variants could yet emerge. Tedros noted that while the official COVID-19 death toll was 7 million, the real figure was estimated to be at least 20 million.
Tedros said the pandemic had been on a downward trend for more than a year, acknowledging that most countries have already returned to life before COVID-19.
He bemoaned the damage that COVID-19 had done to the global community, saying the pandemic had shattered businesses, exacerbated political divisions, led to the spread of misinformation and plunged millions into poverty.
When the U.N. health agency first declared the coronavirus to be an international crisis on Jan. 30, 2020, it hadn’t yet been named COVID-19 and there were no major outbreaks beyond China.
More than three years later, the virus has caused an estimated 764 million cases globally and about 5 billion people have received at least one dose of vaccine.
In the U.S., the public health emergency declaration made regarding COVID-19 is set to expire on May 11, when wide-ranging measures to support the pandemic response, including vaccine mandates, will end. Many other countries, including Germany, France and Britain, dropped most of their provisions against the pandemic last year.
When Tedros declared COVID-19 to be an emergency in 2020, he said his greatest fear was the virus’ potential to spread in countries with weak health systems.
Most recently, WHO has struggled to investigate the origins of the coronavirus, a challenging scientific endeavor that has also become politically fraught.
COVID-19
COVID-19 in Iran: Nearly 900 new cases, 24 deaths recorded

The Iranian health ministry announced on Sunday that more than 890 new cases of COVID-19 have been identified across the country during the past 24 hours, adding that 24 patients have died in the same period of time, Fars News Agency reported.
"A sum of 891 new patients infected with COVID-19 have been identified in the country based on confirmed diagnosis criteria during the past 24 hours," the Iranian Health Ministry's Public Relations Center said on Sunday, adding, "454 patients have been hospitalized during the same time span."
The ministry’s public relations center said 611 people infected with COVID-19 are in critical condition.
COVID-19
China says 200 million treated, pandemic ‘decisively’ beaten

China says more than 200 million of its citizens have been diagnosed and treated for COVID-19 since it lifted strict containment measures beginning in November.
With 800,000 of the most critically ill patients having recovered, China has “decisively beaten” the pandemic, according to notes from a meeting of the ruling Communist Party’s all-powerful Politburo Standing Committee presided over by President and party leader Xi Jinping, AP reported.
China enforced some of the world’s most draconian lockdowns, quarantines and travel restrictions and still faces questions about the origins of the virus that was first detected in the central Chinese city of Wuhan in late 2019. Heavy-handed enforcement prompted rare anti-government protests and took a heavy toll on the world’s second-largest economy.
The official Xinhua News Agency quoted Xi as saying that policies to control the outbreak had been “entirely correct.” The abrupt lifting in November and December of the “zero COVID” policy that had sought to eliminate all cases of the virus led to a surge in infections that temporarily overwhelmed hospitals.
Case numbers have since peaked and life has largely returned to normal, although international travel in and out of China has yet to return to pre-pandemic levels.
China is now transitioning to a post-pandemic stage after a fight against the outbreak that was “extraordinary in the extreme,” Xinhua said.
The government will continue to “optimize and adjust prevention and control policies and measures according to the times and situations with a strong historical responsibility and strong strategic determination,” Xinhua said.
-

 Latest News5 days ago
Latest News5 days agoSouth Korea pledges $5 million to support vulnerable families in Afghanistan
-

 Latest News3 days ago
Latest News3 days agoMinistry: $1 billion invested in Afghanistan’s poultry production sector
-
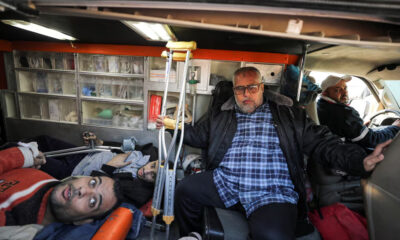
 Regional4 days ago
Regional4 days agoU.N. body accuses Israel of destroying Gaza healthcare
-

 Latest News5 days ago
Latest News5 days agoShah wa Arus dam inaugurated in Kabul
-

 Latest News3 days ago
Latest News3 days agoDeclining water levels affect 50 percent of fish farms in Kandahar
-

 Latest News3 days ago
Latest News3 days agoSalt refinery plant to be built in Takhar province
-

 Latest News4 days ago
Latest News4 days agoAt least 71 killed in Ethiopia road accident
-

 Sport3 days ago
Sport3 days agoAfghanistan set for second test against Zimbabwe in Bulawayo
























