Latest News
More Children Dying in Afghanistan War, Says UN, with Death Toll Up 15 Percent
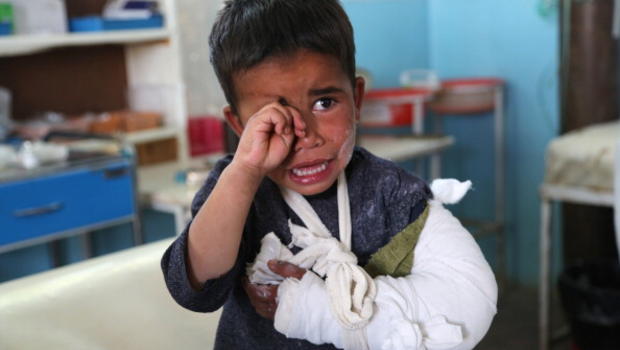
 The number of children killed and injured in Afghanistan’s war has increased in the first nine months of the year, 2016, compared to the previous year, said U.N. Assistance mission in a new report released Wednesday.
The number of children killed and injured in Afghanistan’s war has increased in the first nine months of the year, 2016, compared to the previous year, said U.N. Assistance mission in a new report released Wednesday.
UN mission said it has documented 2,461 casualties among children in 2016 — 639 deaths and 1,822 wounded.
The statistic shows a 15 percent increase comparing to the last year, January-September 2015.
The mission voiced concern over the continuing increase in child casualties, which have risen every year since 2013.
Between Jan. 1 and Sept. 30, UNAMA documented 8,397 conflict-related civilian casualties with 2,562 deaths and 5,835 wounded. That represents a 1 percent decrease, compared to the same period in 2015, said the mission.
Suicide bombings and other attacks, including improvised explosive devices are the main reasons of civilian causalities.
“Increased fighting in densely populated areas makes it imperative for parties to take immediate steps to ensure all feasible precautions are being taken to spare civilians from harm,” the report quoted Tadamichi Yamamoto, the U.N. chief’s special representative for Afghanistan.
Casualties caused by pro-government forces rose 42 percent compared to last year, with 623 deaths and 1,274 injured, U.N. investigators reported.
That includes a spike of 72 percent in casualties from air strikes by the Afghan air force and its international allies.
At least 133 people were killed and 159 were injured in air strikes, with two-thirds of those casualties attributed to the Afghan air force, the U.N. said.
The deadliest areas for civilians are in the traditional Taliban heartland in the south, including Uruzgan, the deeply impoverished, mountainous province that claimed most of the 41 Australian Defense Force personnel who perished during Australia’s combat mission in Afghanistan.
The U.N. report also documented numerous conflict-related incidents targeting health-care and educational facilities, as well as those providing humanitarian aid.
In terms of deaths and injuries, 2013 was the worst year of the war for Afghan women and children, with most of the casualties caused by either stepping on or driving over roadside bombs or getting caught in fighting.
But the deadliest year of the war were 2011 and 2016, when 3,133 civilians died as the Taliban launched a fierce pushback with roadside bombs and other attacks against the increased number of international forces who wrested back much of the territory controlled by the insurgents and in 2016 the bloody year for civilians when they marched in a protest for transferring power from central areas of the country.

Latest News
Health Minister slams deportations, says neighbors cannot accept Afghanistan’s progress
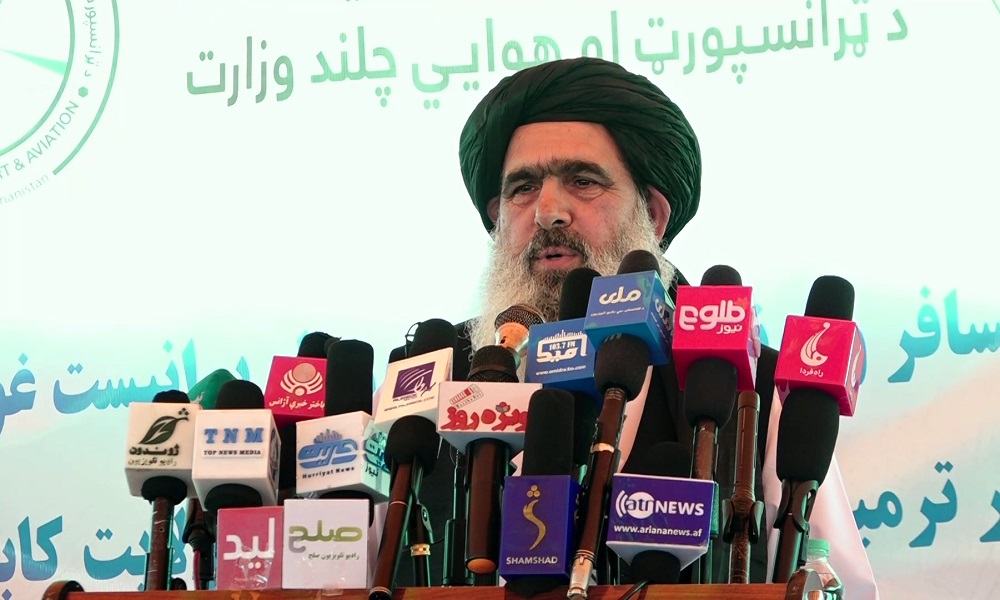

Acting Minister of Public Health Noor Jalal Jalali said on Sunday that Afghanistan’s neighbors cannot tolerate Afghanistan’s progress, so they harass migrants, confiscate their property and forcibly expel them.
“One has built a house and a life with his own power, but he is told that he has no right to take it with him,” Noor Jalal Jalali said at an event in Kabul. “He is beaten, humiliated and taken to a vehicle and is told to leave. Our brothers should return to their country even with the little money they have.”
Pakistan plans to expel three million Afghans from the country this year. Arrests have already begun in several cities.
Local officials in Nangarhar province say 316 families have entered the country through the Torkham crossing in the past three days.
“All the committees are ready,” said Azizullah Mustafa, deputy governor of Nangarhar. “In the last two or three days, 316 families have been expelled. There is the service committee. We have also contacted the center. Allah willing, we have the facilities. We will also meet with institutions to coordinate the process.”
About 845,000 Afghans have left Pakistan over the past 18 months, figures from the International Organization for Migration show.
The deportations come despite criticism from human rights groups.
Latest News
Thousands of local tourists flock to Balkh over Eid-ul-Fitr
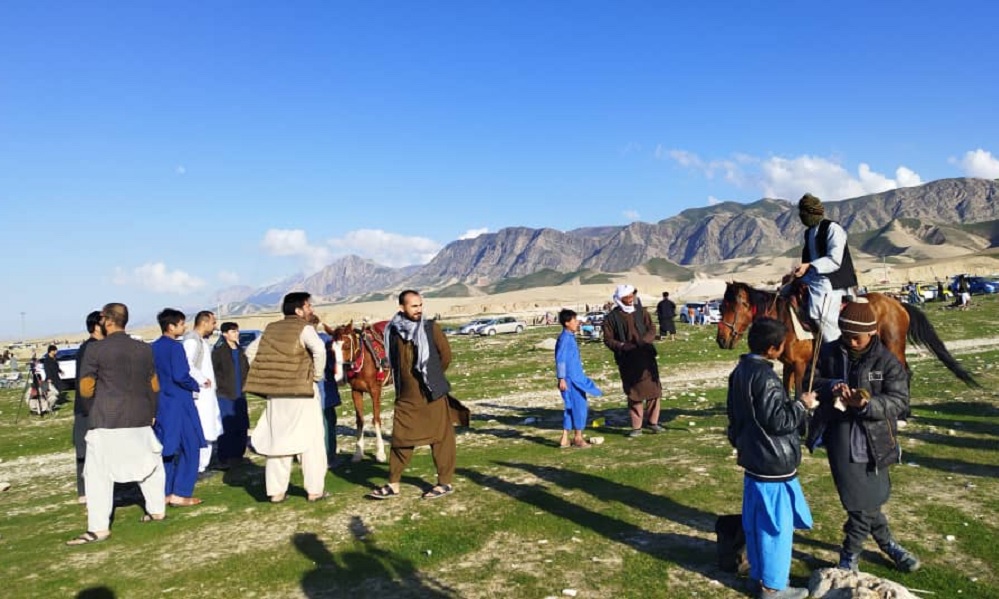

More than 12,000 local tourists, along with 21 foreigners, visited Balkh province in northern Afghanistan over Eid-ul-Fitr, Balkh Information and Culture Department officials confirmed.
According to the officials, the tourists visited recreational areas and historical sites during the three-day Eid holiday period.
Tourists visiting the province said they were happy about the improved security situation but called for more recreational areas.
One popular area was Marmul district, which lies about 20 km west of Mazar-e-Sharif, the provincial capital. Visitors said however they would have liked to see more restaurants, mosques, markets and other facilities.
Local officials in Balkh said efforts are being made to create facilities in recreational areas in the province.
In addition to Marmul, other popular destinations in Balkh for visitors this Eid was the Qosh Tepa Canal, Dasht-e-Shadian, Amu River and Chashma-e-Khaja Sikandar.
Latest News
UN rights experts call on Pakistan to stop removal process of Afghan refugees
The experts urged Islamabad to immediately stop mass internal relocations, deportations, arrests, evictions, intimidation and other pressures on Afghans
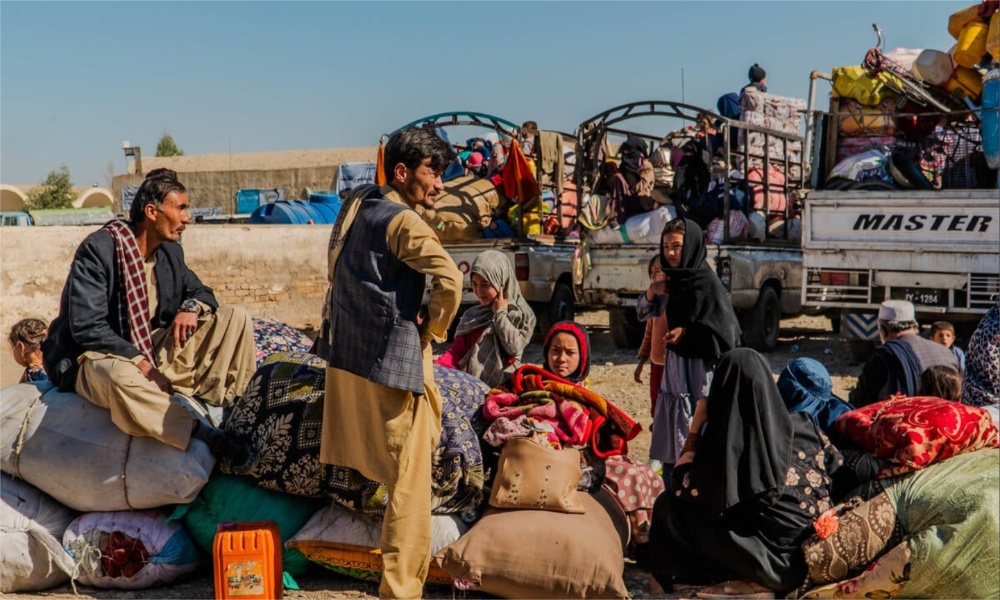

UN human rights experts have called on the Pakistan government to stop their plans to forcibly remove Afghans from the cities of Islamabad and Rawalpindi, nor to deport them to Afghanistan.
According to a statement issued on Friday, the UN experts (as listed below) called on Pakistan to continue its important role as a neighboring country with a long history of hosting Afghan refugees.
The deadline for their voluntary departure was set for 31 March, but Islamabad moved the deadline by a few days to take Eid-ul-Fitr into account.
“Millions of Afghans in Pakistan are at risk of being pushed back to Afghanistan without regard for their genuine protection concerns – including gender-based violence and the systematic dismantling of the rights of women and girls – in violation of international human rights law and refugee law, and disregarding UNHCR’s non-return advisory,” the experts said.
“We urge Pakistan to immediately stop mass internal relocations, deportations, arrests, evictions, intimidation and other pressures on Afghans to cross the border into Afghanistan, and to uphold the absolute and non-derogable principle of non-refoulement,” they said.
The experts expressed particular concern about the gendered and intersectional impact.
The UN experts have repeatedly spoken out against Pakistan’s Illegal Foreigners’ Repatriation Plan of September 2023, which has already pressured hundreds of thousands of Afghans to uproot their lives and return to Afghanistan.
Ahead of the 31 March deadline, the UN documented a worrying increase in arrests of Afghans. Many desperate Afghans have contacted the experts, fearing persecution by the Taliban in Afghanistan if they are forced to return.
“The most vulnerable are Afghan women, girls, LGBTI persons, ethnic and religious minorities, former government officials and security personnel, human rights defenders, and media workers,” the experts said.
“Children, especially unaccompanied, are at heightened risk of trafficking, child marriage and abuse, while persons with disabilities and older persons are also particularly vulnerable. They should all be individually assessed.”
The experts expressed concern about returns of Afghans to Afghanistan from other countries, potentially contravening international human rights and refugee law.
The experts also acknowledged security risks, including terrorist attacks in Afghanistan, as well as Pakistan.
The experts noted that many Afghans who had left for Pakistan, having been given reasonable expectations of being resettled in a third country, had their dreams of a secure future shattered by the sudden halt of resettlement programmes.
They stressed that funding cuts will reduce the ability of the de facto authorities in Afghanistan, together with humanitarian agencies, to support a large influx of people from neighboring countries.
“Abrupt and drastic funding cuts by donors are already having a severe impact on much-needed humanitarian assistance to Afghans,” the experts said.
“Given the deteriorating human rights situation in Afghanistan, durable solutions are needed for Afghans outside the country, with strong support from the broader international community.”
The experts are as follows:
Richard Bennett, Special Rapporteur on the human rights situation in Afghanistan; Siobhán Mullally, Special Rapporteur on trafficking in persons, especially women and children; Laura Nyirinkindi (Chair), Claudia Flores (Vice-Chair), Dorothy Estrada Tanck, Ivana Krstić, and Haina Lu, Working group on discrimination against women and girls; Ben Saul, Special Rapporteur on the promotion and protection of human rights and fundamental freedoms while countering terrorism; Reem Alsalem, Special Rapporteur on violence against women and girls, its causes and consequences; and Balakrishnan Rajagopal, Special Rapporteur on the right to adequate housing.
-

 Latest News5 days ago
Latest News5 days agoMinistry of Economy calls on US to release Afghanistan’s frozen funds
-

 Latest News4 days ago
Latest News4 days agoPakistan ‘extends’ deadline for a week for Afghans to leave the country
-

 World5 days ago
World5 days agoAs Iran tensions build, US military moves warplanes to reinforce Middle East
-

 Sport5 days ago
Sport5 days agoIPL 2025: Batters in race for prestigious Orange Cap
-

 Latest News4 days ago
Latest News4 days agoPanjshir to Kabul water conduit project ‘waiting for budget approval’
-

 Latest News4 days ago
Latest News4 days agoFemale journalists complain about lack of access to accurate and timely information
-

 Business4 days ago
Business4 days agoExports to Pakistan grind to a halt over faulty scanner at Torkham
-

 Regional4 days ago
Regional4 days agoMilitary confrontation seems inevitable if no new Iran nuclear deal, France says














